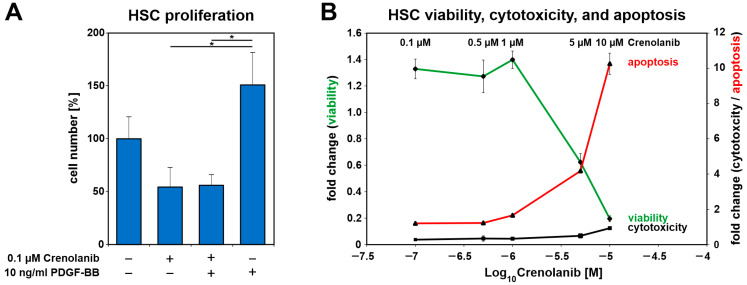
Figure 3.
Crenolanib (≤1 µM) treatment inhibited PDGF-BB-mediated cell proliferation without adverse effects on HSC viability. (A) The proliferation of freshly isolated HSC in primary culture after Crenolanib (0.1 µM) and PDGF-BB (10 ng/mL) treatment was assessed after 72 h by cell counting under serum-free conditions (n = 3–4). PDGF-BB promoted the proliferation of HSC whereas Crenolanib inhibited PDGF-BB-mediated cell proliferation. (B) HSC survival was analyzed by the ApoTox-Glo assay after treatment with various concentrations of Crenolanib for 24 h (n = 4). Cell viability was assessed after the addition of the substrate GF-AFC, which is converted into a fluorescent dye by proteases, such as cathepsin C. The cytotoxicity of Crenolanib was determined using bis-AAF-R110, which is cleaved by proteases, such as tripeptidyl peptidase II, when the dye enters dying cells [44]. Apoptosis was measured in this experimental setup by determining caspase 3/7 activity. The data indicated that Crenolanib exerted no obvious adverse effects at the concentrations used in this study (0.1–1 µM). HSC survival was affected at concentrations of 5 and 10 µM Crenolanib.