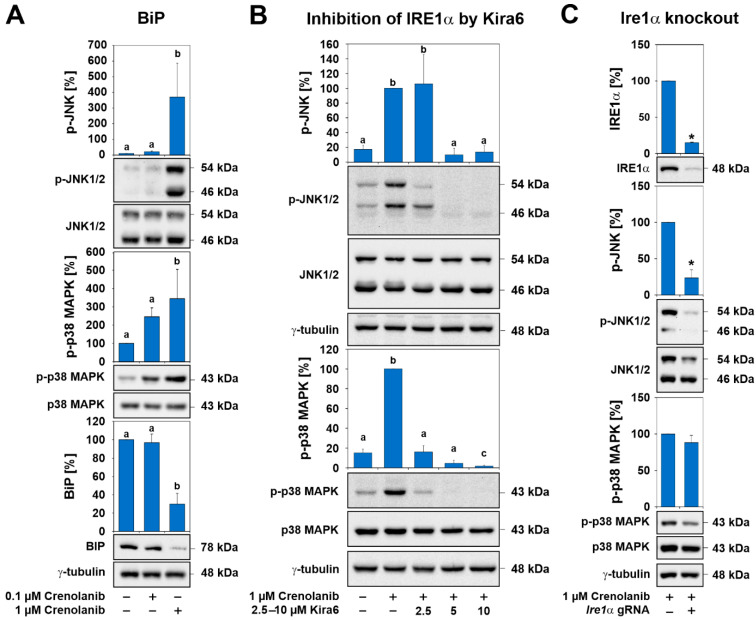
Figure 6.
The effects of Crenolanib are mediated by a stress response via IRE1α. (A) The stimulation of culture-activated HSC with 0.1 and 1 µM Crenolanib for 7 days and the subsequent analysis of p-p38 MAPK, p-JNK, and binding immunoglobulin protein (BiP) by Western blot. Long-term exposure of HSC to 1 µM Crenolanib significantly lowered BiP levels by 70%. At this concentration, Crenolanib has also the greatest impact on JNK and p38 MAPK activation. (B) The inhibition of IRE1α by Kira6 in HSC significantly prevented the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and JNK, as shown by Western blot analysis. (C) The CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout of Ire1α in HSC significantly reduced the Crenolanib-mediated phosphorylation of JNK but not p38 MAPK in comparison to the mock control, which was set to 100%. For densitometry, the protein bands for total p38 MAPK, total JNK, and γ-tubulin were used as references (n = 3; p < 0.05; significant differences are indicated by different letters or *asterisks).