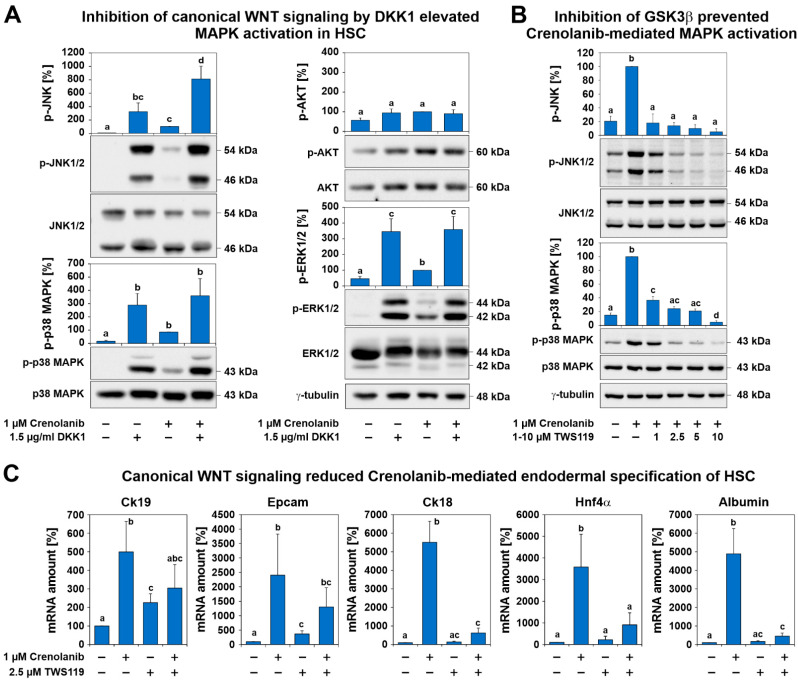
Figure 7.
Canonical WNT signaling prevented the activation of signaling cascades associated with proliferation and differentiation, supporting quiescence in HSC. (A) Culture-activated HSC were treated with 1.5 µg/mL dickkopf 1(DDK1) for 1 h prior to 1 µM Crenolanib administration. The inhibition of canonical WNT signaling by DDK1 resulted in the increased phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, JNK, and ERK1/2, as assessed by Western blot analysis, even in the absence of Crenolanib, whereas AKT signaling was weakly affected. Crenolanib significantly elevated the phosphorylation of JNK (n = 3; p < 0.05). (B) HSC were pretreated with the GSK3β inhibitor TWS119, which reduces β-catenin degradation and promotes canonical WNT signaling. This approach significantly reduced the activation of p38 MAPK and JNK in response to Crenolanib. The results of the Crenolanib-treated group were set to 100% in the densitometry analysis of the Western blots (n = 3). (C) The expression analysis of HSC treated with Crenolanib for 7 days in the presence or absence of 2.5 µM TWS119. The Crenolanib-induced expression of hepatocyte markers Ck18, Hnf4α, and albumin was inhibited by TWS119, as measured by qPCR. The progenitor markers Epcam and Ck19 were only slightly suppressed (n = 4; p < 0.05; significant differences are indicated by different letters).