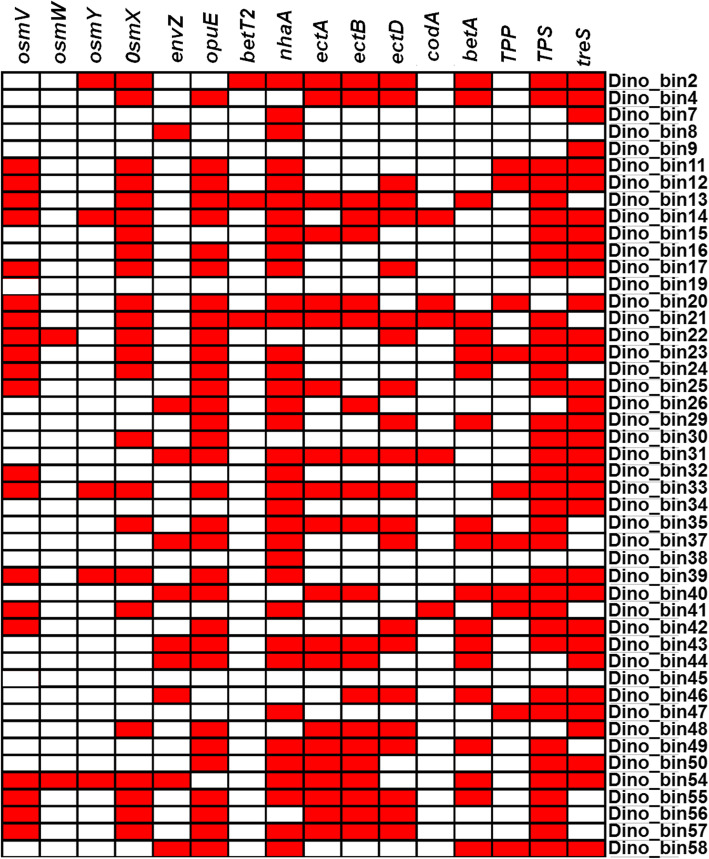
Fig. 4.
Presence of functional genes (red) in MAGs involved in coping with high osmolality in the dinosaur fossil bone. Gene abbreviations: osmolarity sensor protein (envZ), osmotically-inducible protein (osmY), osmoprotectant import ATP-binding proteins (osmW and osmV), osmoprotectant-binding protein (osmX), and osmoregulated proline transporter (opuE), osmo-dependent choline transporter (betT2), Na(+)/H(+) antiporter (nhaA), L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid acetyltransferase (ectA), ectoine synthase (ectC), ectoine hydroxylase (ectD), glycine-betaine producing choline oxidase (codA), oxygen-dependent choline dehydrogenase (betA), trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase (TPP), trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) and trehalose synthase (treS)