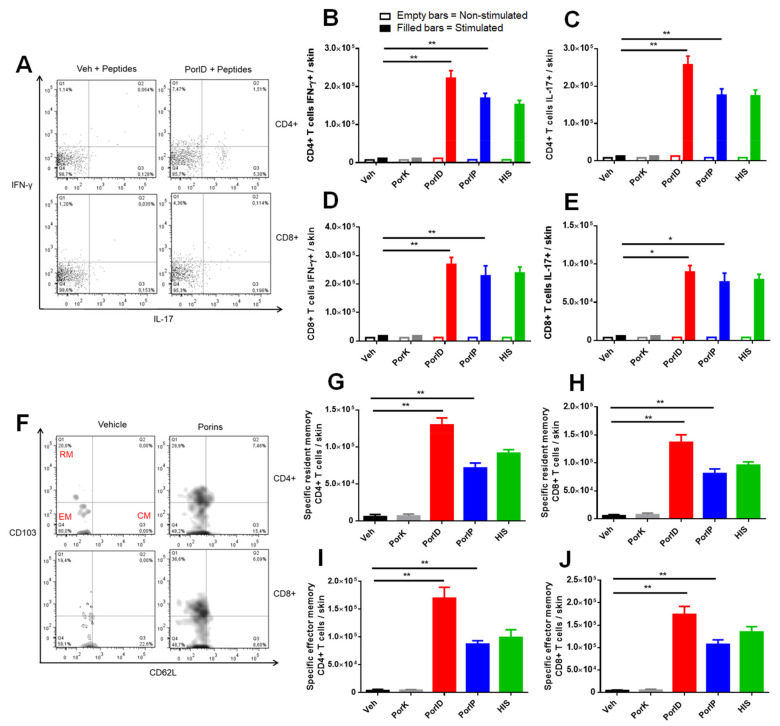
Figure 2.
Vaccination with S. Typhi porins induces functional resident and effector memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses. C57BL/6J mice were injected intradermally in the ear with vehicle (Veh), proteinase K-digested porins (PorK), porins (PorID), or intraperitoneally with porins (PorIP) or heat-inactivated S. Typhi (HIS) at day 0. All groups were boosted at day 14 with porins injected intradermally in the ear. At day 28, expression of IFN-γ and IL-17 was evaluated in skin T cells following stimulation with S. Typhi porins peptides. Representative plot (A) used to analyze the total number of IFN-γ + (B) and IL-17+ (C) CD4+ T cells. Total number of IFN-γ + (D) and IL-17+ (E) CD8+ T cells. At day 28, memory phenotype T cells (CD44+) were evaluated in the skin. Representative plot (F) used for the detection of both effector memory (CD62L−, CD103−) (G,H) and resident memory (CD62L−,CD103+) (I, J) CD4+ and CD8+ T cell populations, respectively (CM, central memory, EM, effector memory, RM, resident memory) (n = 7; 2 independent experiments; significant difference for a Kruskal–Wallis test ** p < 0.05 * p < 0.1 with Dunn´s multiple comparison).