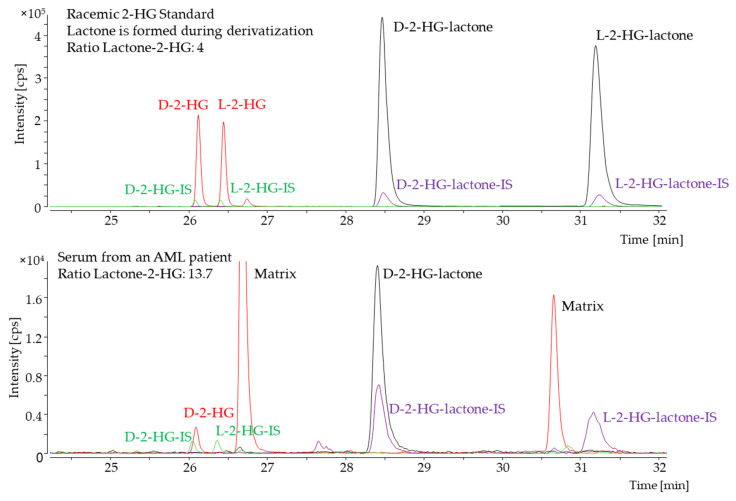
Figure 2.
Chiral GC–MS analysis. The red trace shows the extracted ion chromatogram for the D- and L-enantiomer of the 2-HG derivative. The corresponding stable isotope-labeled internal standard (IS) is shown in green. The extracted ion chromatogram for the D- and L-enantiomer of the 2-HG-lactone derivative is shown in black, and the corresponding IS-trace in purple. The upper panel shows a racemic D/L-2-HG standard, and the lower panel shows a serum sample of an acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patient with an IDH2-R140Q mutation. For standard solutions, the ratio of each enantiomer of 2-HG and -lactone was found to be consistent. For the serum sample, both L-enantiomers were hardly detectable, while the ratio of D-lactone/2-HG was found to be increased for the unlabeled analyte.