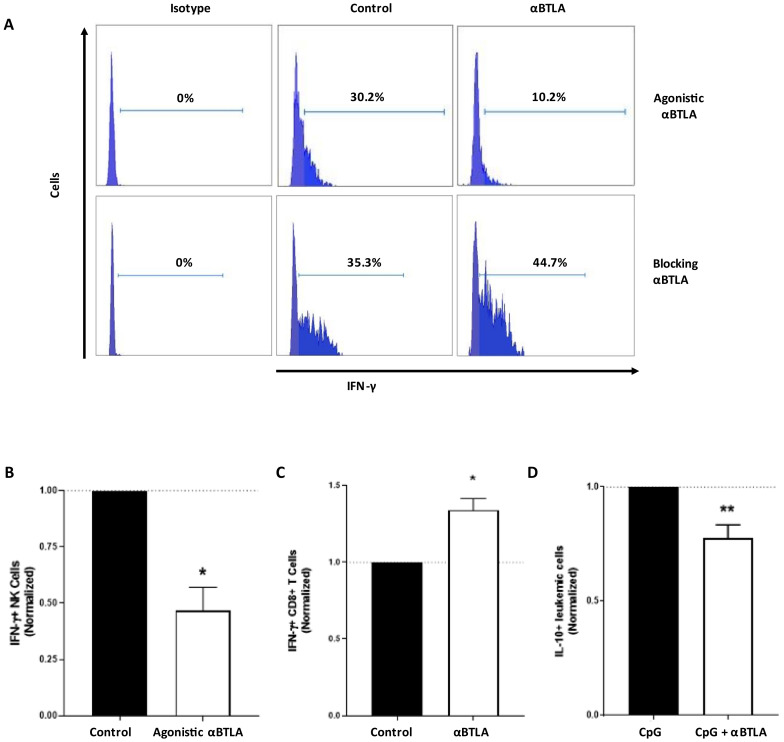
Figure 6.
BTLA induces NK cell immunosuppression, but it may be reverted by BTLA/HVEM axis disruption. (A) Representative flow cytometry histograms of IFN-γ+ NK cells from patients with CLL treated with agonistic or blocking anti-BTLA mAb. (B) PBMCs from patients with CLL were cultured with plate-coated agonistic anti-BTLA or control IgG (10 µg/mL) for 24 h (n = 6) and IFN-γ+ NK cells were assessed by flow cytometry (normalized to control). (C) PBMCs from patients were treated with blocking anti-BTLA or isotype-matched IgG (10 µg/mL) for 72 h and IFN-γ+ NK cells were evaluated by flow cytometry (n = 7) (normalized to control). (D) PBMCs from patients with CLL were treated with CpG (200 ng/mL) alone or in combination with blocking anti-BTLA or control IgG (10 µg/mL) for 72 h and IL-10+ leukemic cells were evaluated by flow cytometry (n = 8) (normalized to CpG-treated PBMCs). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.