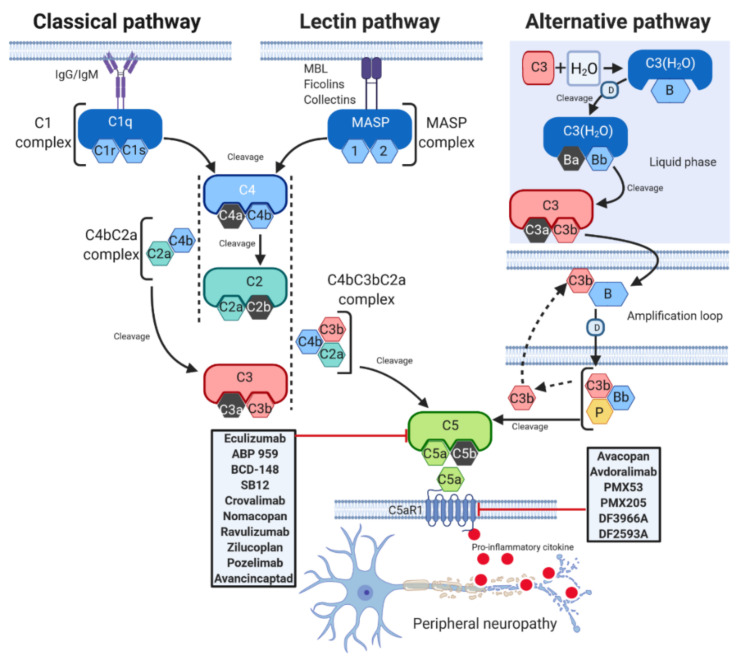
Figure 1.
C5a complement activation pathways. The C5a complement system can be activated through three pathways: classical (CP), lectin (LP), and alternative (AP). CP begins with antibody-mediated activation of C1 complex, which leads to formation of the C4bC2a complex, the C3 convertase. This C3 convertase cleaves C3 to produce C3b, which forms a complex with C4b and C2a. This complex is the C5 convertase, which cleaves C5 to produce C5a and C5b. The LP begins with signal recognition by oligomeric structures of mannose- binding lectin (MBL), ficolins and collectins, which activate mannan-binding lectin serine proteases (MASP) 1 and 2, which in turn mediate the production of C4b. From this point, the LP follows the same steps as the CP. In the AP, C3 interacts with factor B (B) and factor D (D), leading to cleavage of further C3, and this process is perpetuated through an amplification loop. In the final step of this pathway, even properdin (P) is involved. Additional C3b binds to the C3 convertase and forms a C5 convertase, which cleaves C5 to form C5a and C5b. C5a activates on C5aR1, a prototypical G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) recruiting immune cells to the site of inflammation. Drugs targeting C5 or C5aR1 in different stage of development are reported in the gray rectangles. T-arrow indicates inhibition of pathway at point of intersection.