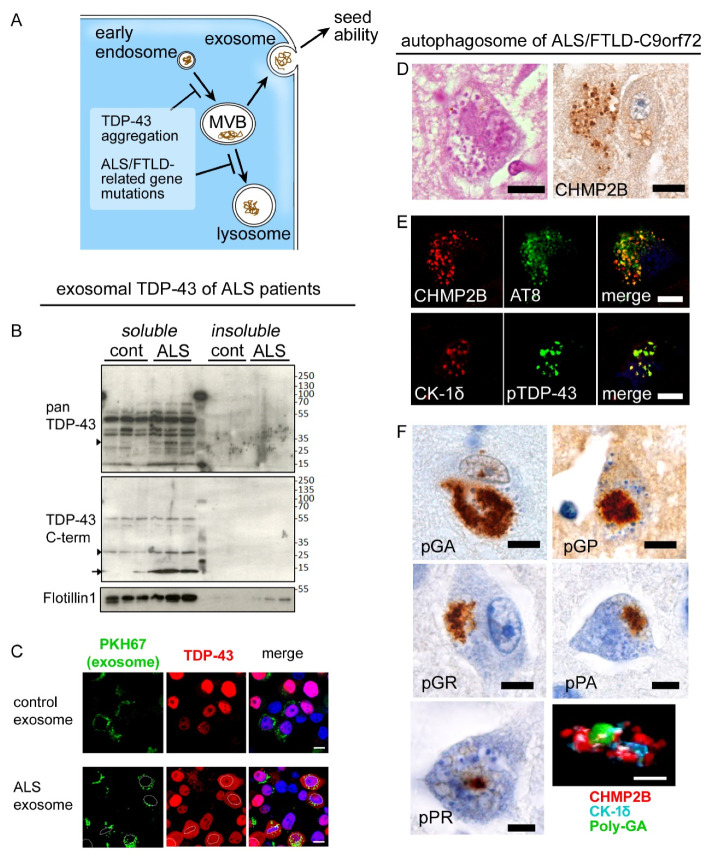
Figure 4.
Endosome-autophagosome system and TDP-43 pathology. (A) Aggregated TDP-43 and dysfunction/haploinsufficiency of ALS/FTLD-TDP-related genes have been reported to impair maturation, transport, or fusion of endosomal and autophagosomal vesicles. (B) The exosomal fraction of brain lysates from ALS-TDP patients contains abundant TDP-43, particularly C-terminal fragments. (C) Neuro2a cells that were treated with ALS-patients-derived exosome and transfected with human-derived TDP-43 exhibited cytoplasmic aggregation of TDP-43. (D–F) These panels show neuropathologic changes of ALS/FTLD-TDP patients carrying C9-orf72 hexanucleotide expansions. Hippocampal pyramidal neurons often displayed granulovacuolar degeneration (GVD) that was associated with immunoreactivity for CHMP2B, a marker of multivesicular bodies (MVBs) (D). GVD granules, which were immunolabeled with CHMP2B and CK1δ, contained p-TDP-43 and hyperphosphorylated tau (E). Mutation-derived sense (poly GA, poly GP, and poly GR) and antisense dipeptides (poly PR and poly PA) were frequently covered with CHMP2B-immunopositive GVD granules. Scale bars: 10 μm.