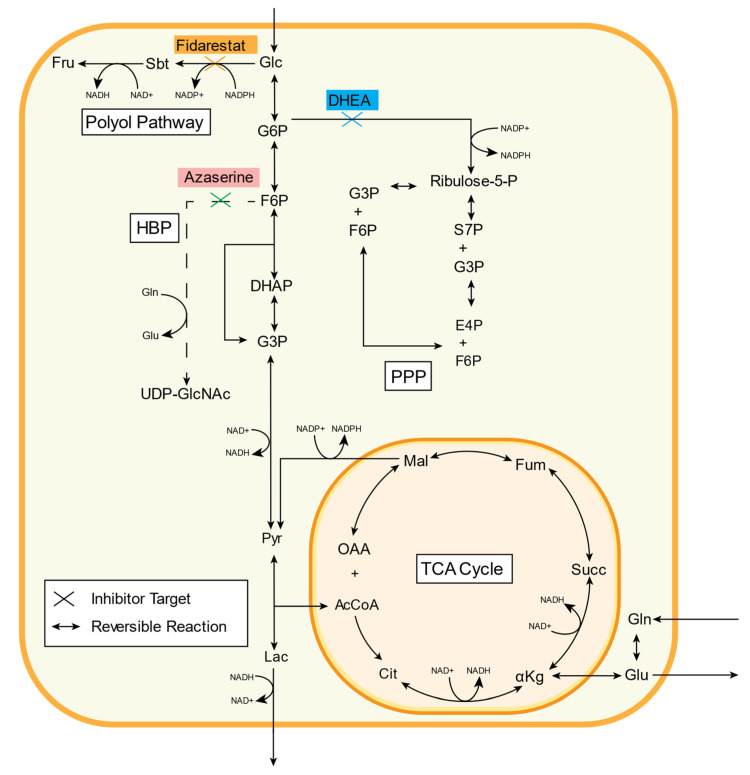
Figure 1.
Three inhibitors (fidarestat, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and azaserine) were used to decrease glucose flux down glycolytic side branch pathways (polyol, PPP, and HBP, respectively). Fidarestat inhibits aldose reductase, an enzyme that catalyzes the first rate-limiting step of the polyol pathway and reduces glucose to sorbitol. DHEA inhibits glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), an enzyme involved in converting glucose-6P into 6P-glucolactone in the PPP. Azaserine inhibits the rate-limiting enzyme GFAT in the HBP, a pathway responsible for producing UDP-GlcNAc. See Table 1 for metabolite abbreviations.