Figure 3.
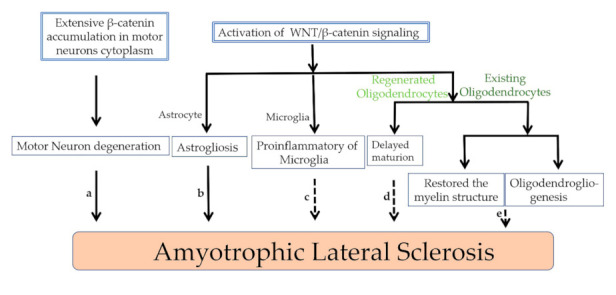
WNT/β–catenin signaling and β–catenin protein contribute to the onset of ALS. a. The extensive accumulation of β-catenin in motor neurons results in the degeneration of motor neurons in ALS. b. Activation of WNT/β–catenin signaling affects astrogliosis in ALS. c. Activation of WNT/β–catenin signaling promotes the transformation of microglia to proinflammatory phenotype. d. Activation of WNT/β–catenin signaling delays the maturation of regenerated oligodendrocytes. e. For the existing oligodendrocytes, activation of WNT/β–catenin signaling promotes the restored of degenerative myelin structure and oligodendrogliogenesis. Black arrows represent confirmed phenomena in ALS; dashed arrows illustrate hypothetical models in ALS.
