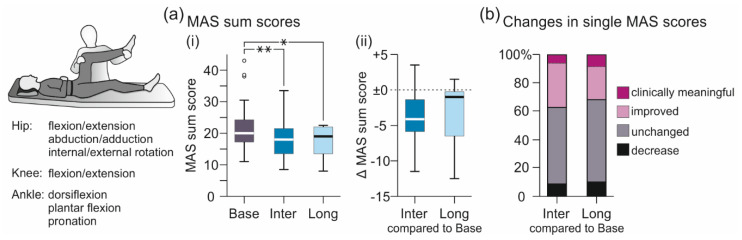
Figure 2.
Intermediate and longer-lasting carry-over effects of transcutaneous spinal cord stimulation on the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS)-based evaluation of lower-extremity muscle hypertonia. (a) Group results of (i) MAS sum scores obtained in Base, Inter, and Long; and (ii) changes in MAS sum scores per participant in Inter and Long compared to Base, illustrated by box plots. Bold horizontal lines within boxes are medians; boxes span the interquartile range. Whiskers extend to the lowest and largest values that are not outliers (illustrated as circles; see Methods). Brackets and asterisks denote significant results of post-hoc pairwise comparisons (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.001). (b) Changes in individual MAS scores (one score per movement, limb, and participant) in Inter and Long compared to Base. Stacked bar charts show percentage of changes classified as clinically meaningful improvement (reduction by ≥ 1; magenta sections of bars); improvement (reduction by 0.5; light magenta); unchanged (grey); and increase (black). Base, baseline evaluation comprising two assessments conducted ~24 h and immediately pre-intervention; Inter, evaluation of intermediate carry-over effects comprising two assessments immediately and two hours post-intervention; Long, evaluation of longer-lasting carry-over effects conducted ~24 h after the stimulation session; MAS, Modified Ashworth Scale.