Figure 3.
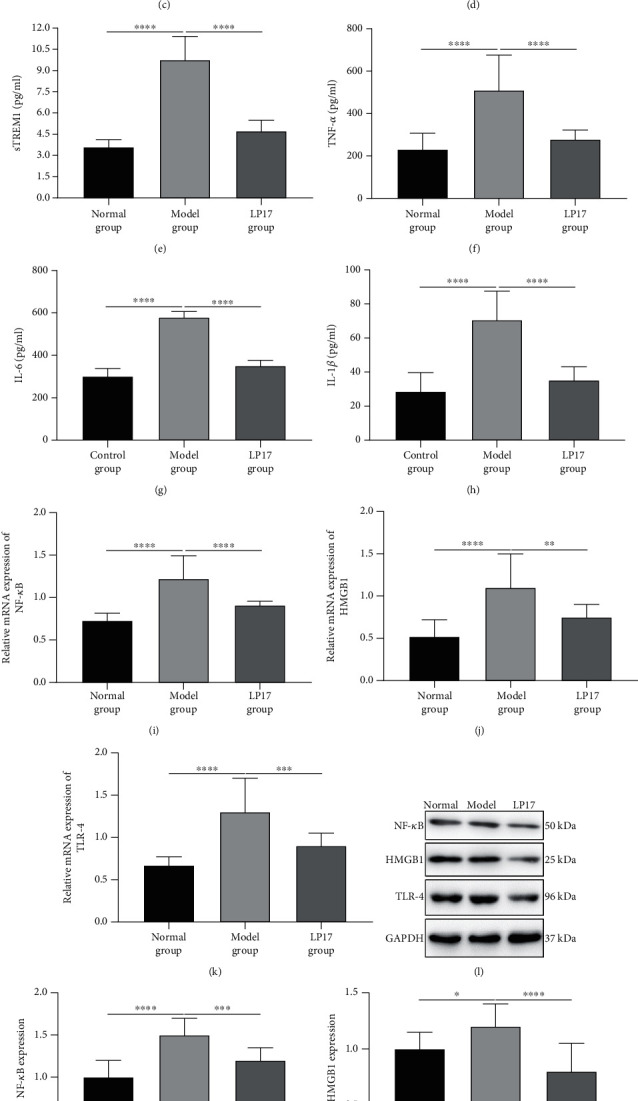
LP17 reduces inflammatory response and activation of the NF-κB signaling in LPS-induced acute intestinal dysfunction rats. (a–d) The levels of (a) soluble TREM1 (sTREM1; F value = 40.98), (b) TNF-α (F value = 39.30), (c) IL-6 (F value = 231.5), and (d) IL-1β (F value = 186.3) in the plasma samples of rats from the indicated groups at 36 h after LPS treatment for 3 days were measured by ELISA. (e–h) The levels of (e) sTREM1 (F value = 121.6), (f) TNF-α (F value = 26.85), (g) IL-6 (F value = 310.5), and (h) IL-1β (F value = 44.45) in the intestine tissue samples of rats from the indicated groups at 36 h after LPS treatment for 3 days were measured by ELISA. (i–k) The mRNA levels of (i) NF-κB (F value = 42.46), (j) HMGB1 (F value = 16.10), and (k) TLR-4 (F value = 22.17) in the small intestine tissues of rats from the indicated groups at 36 h after LPS treatments for 3 days were determined by RT-qPCR. n = 20 for the normal group; n = 14 for the model group; n = 17 for the LP17 group. (l) Representative images of western blot results for NF-κB, HMGB1, and TLR-4 in the small intestine tissues of rats from the indicated groups. (m–o) The expression levels of (m) NF-κB (F value = 25.95), (n) HMGB1 (F value = 13.44), and (o) TLR-4 (F value = 360.2) proteins were quantified according to the western blot results. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for multiple comparisons, followed by Tukey's test. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
