Figure 1.
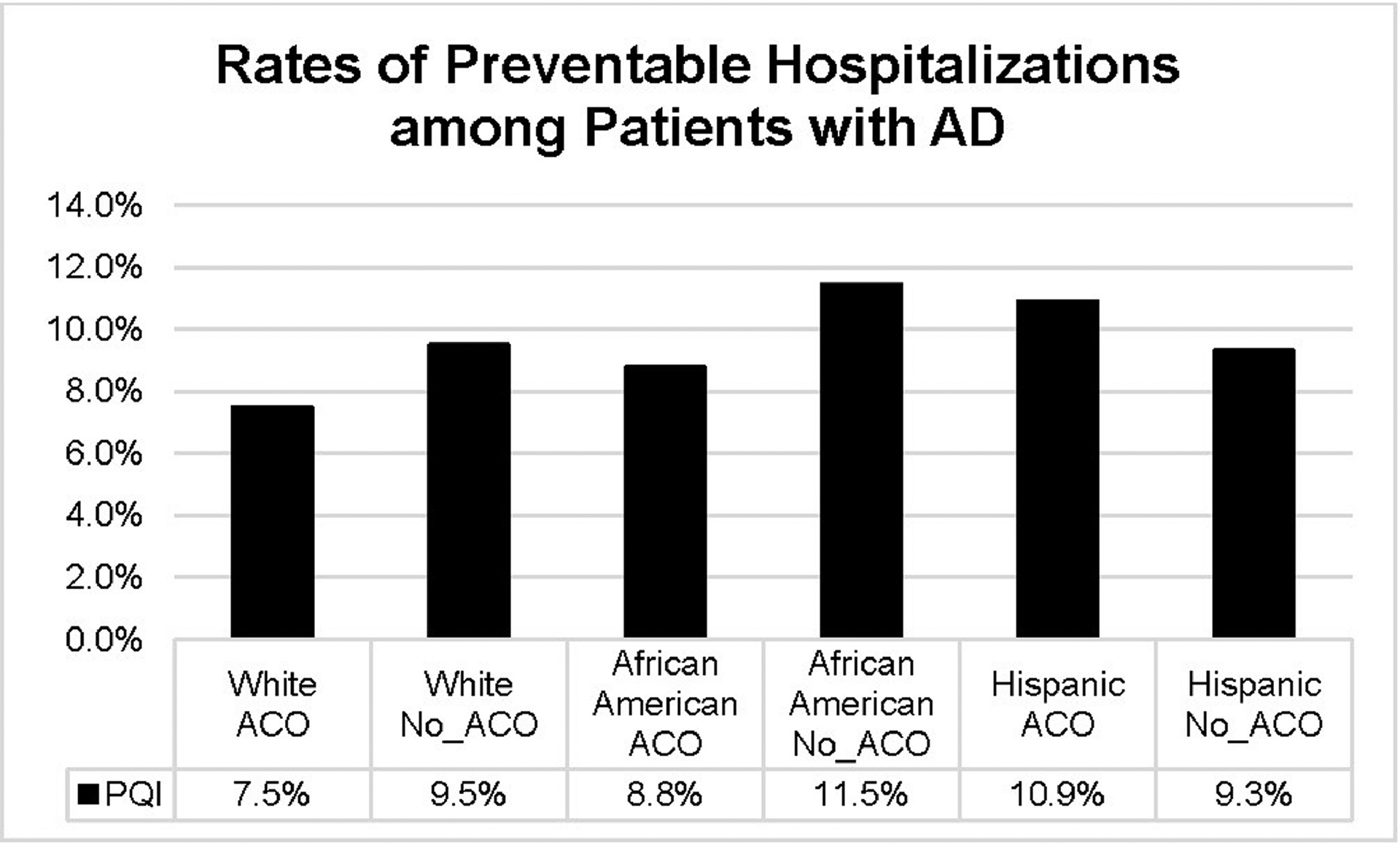
Rates of potentially preventable hospitalization among patients with Alzheimer’s disease by race/ethnicity and ACO affiliation.
Notes: Potentially preventable hospitalization was measured as any of the following AHRQ PQI indicators: uncontrolled diabetes (PQI 14), diabetes-related short-term and long-term complications (PQI 1, PQI 3), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma (PQI 5), hypertension (PQI 7), and heart failure (PQI 8). Total of 629 hospitals were included in11 states after merging the HCUP SID with the AHA annual survey.
ACO, accountable care organization; AD, Alzheimer disease; AHA, American Hospital Association; AHRQ, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; HCUP, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project; PQI, prevention quality indicators; SID, state inpatient databases.
