Figure 5. amiRNA 4-138 line and erf34/erf35 double mutant are sensitive to cadmium.
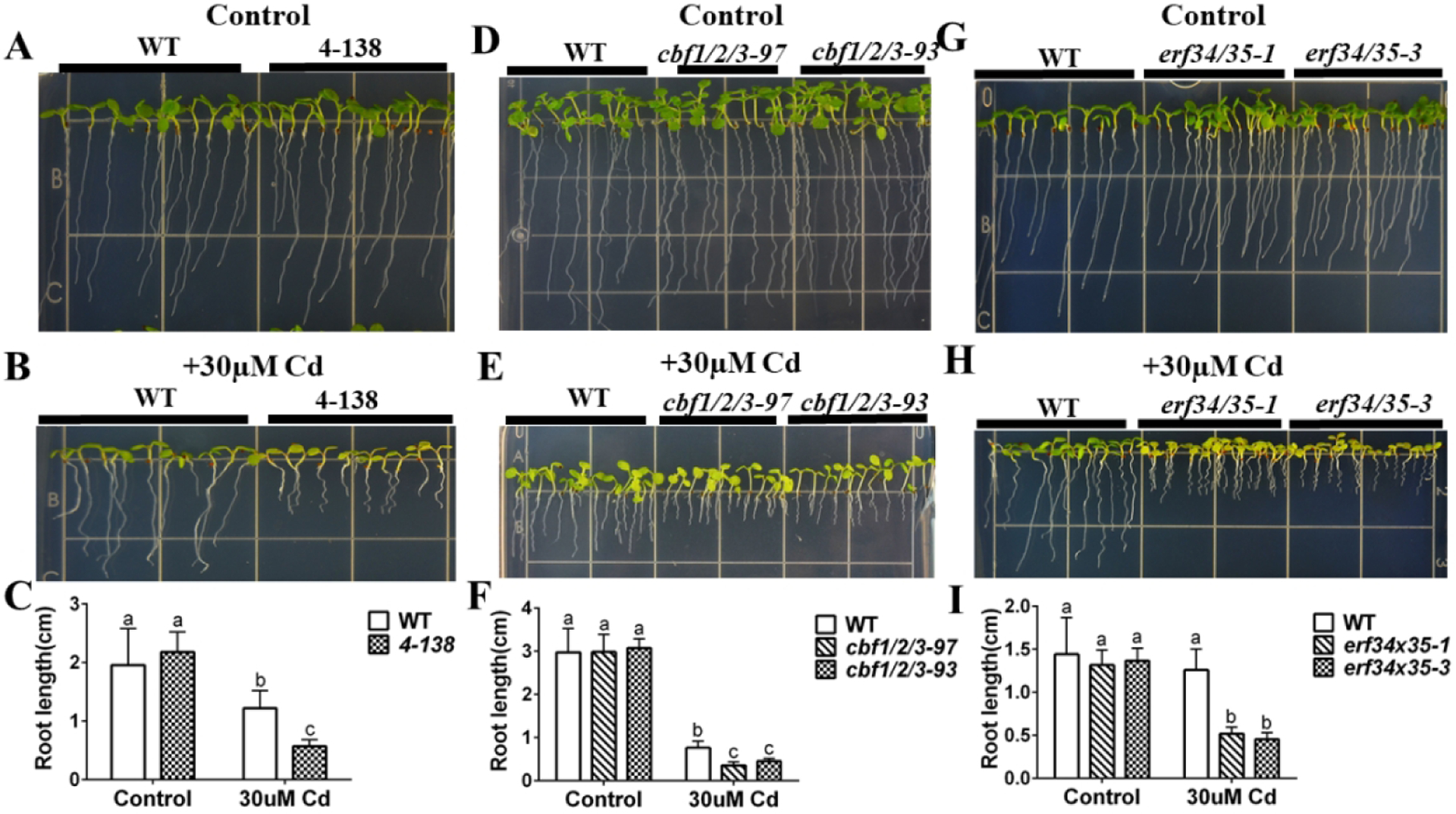
(A), (B) amiRNA line 4-138 shows enhanced cadmium sensitivity in root growth and yellowing of leaves compared to WT: WT and 4-138 amiRNA lines were grown vertically on minimal plates with 1% sucrose plates without (control) or with 30 μM cadmium for 7 days; (C) Primary root lengths of the amiRNA 4-138 line were significantly shorter than WT on cadmium-containing plates. (n=16 seedlings, means ± s.e.m.). (D), (E) CRISPR lines targeting CBF1/2/3 genes show cadmium sensitive phenotypes. WT and CRISPR lines targeting CBF1/2/3 genes were grown vertically on minimal plates with 1% sucrose plates without (control) or with 30 μM cadmium for 7 days; (F) Primary root length of CRISPR lines in CBF1/2/3 genes compared to WT on control and cadmium-containing plates. (n=11 seedlings, means ± s.e.m.). (G), (H) erf34/35 double mutant shows cadmium sensitive phenotype: WT and erf34/35-3 T-DNA double mutant were grown vertically on minimal plates with 1% sucrose plates without (control) or with 30 μM cadmium for 7 days; (I) Primary root length of erf34/35 compared to WT on control and cadmium-containing plates. (n=17 seedlings, means ± s.e.m.). Letters at the top of columns are grouped based on two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, P < 0.05).
