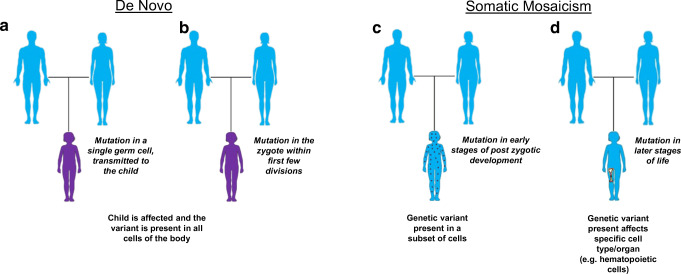
Fig. 1.
Types of sporadic gene mutations leading to disease. (a, b) De novo variants in affected individuals arising from (a) mutations in paternal or maternal germline cells or (b) post-zygotic mutational events occurring within the first few cell divisions. (c, d) Somatic mosaicism with patients having than one DNA sequence arising from post-zygotic mutations occurring at (c) early stages of embryogenesis, leading to the presence of mutations in a subset of cells from multiple lineages or (d) later stages of development or in adulthood, with mosaicism restriction to a specific cell type/tissue, for example hematopoietic stem cells shown here. Images modified from Servier Medical Art, provided by Les Laboratoires Servier