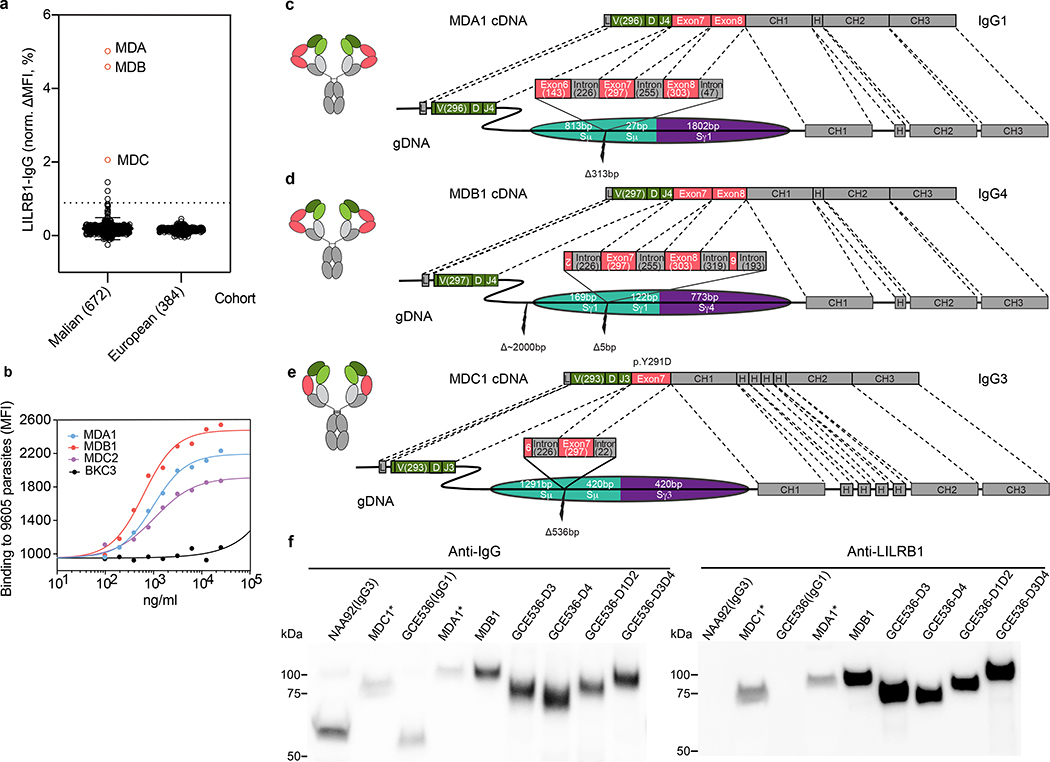
Fig. 1 |. Isolation and identification of LILRB1-containing antibodies from a Malian cohort.
a, Prevalence of LILRB1-containing IgG in plasma of Malian donors compared to a control cohort of European individuals. Donors from whom LILRB1-containing antibodies were isolated are shown in red. The error bars indicate the standard deviation. A cutoff set at normalized ΔMFI = 1% was used to identify donors with detectable levels of LILRB1-containing antibodies. b, Binding of LILRB1-containing monoclonal antibodies to erythrocyte infected by the 9605 parasite isolate (representative of n = 3 independent experiments). An antibody of irrelevant specificity was used as negative control (BKC3). c-e, cDNA and genomic DNA organization in representative B cell clones from 3 donors. LILRB1 inserted DNA segments are colored in red (exons) or dark gray (introns); numbers in brackets indicate the length of inserted nucleotides; adjacent switch regions are shown in teal and purple. Antibody variable domain (VH), green; light chain (VL), light green; CH, dark gray; CL, light gray. f, Western blot analysis of naturally occurring LILRB1-containing antibodies (MDC1 and MDA1 tested as culture supernatants and MDB1 tested as recombinant antibody). Shown are also IgG1 and IgG3 isotype control antibodies (GCE536 and NAA92), as well as recombinant antibodies carrying different LILRB1 domains inserted in the GCE536 VH-CH1 elbow (representative of n = 2 independent experiments). For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.