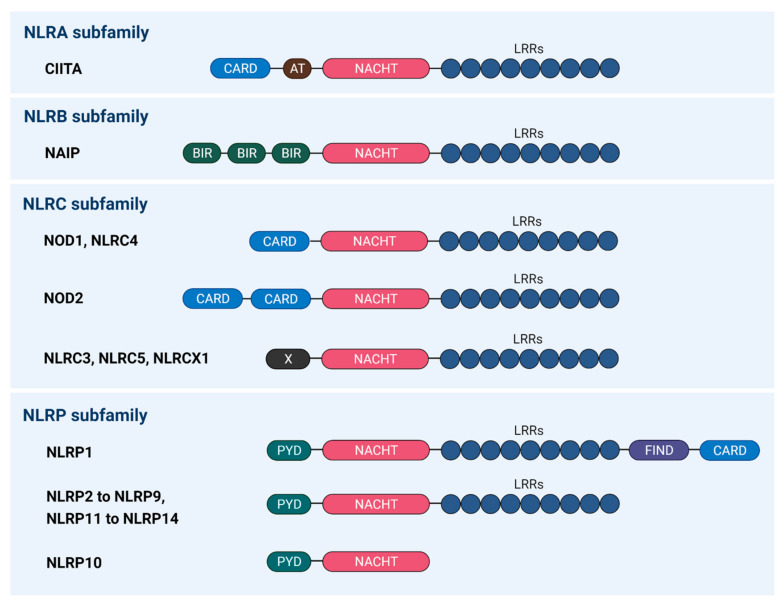
Figure 1.
Human NLR subfamilies and their members. The canonical structure of the NLR consists of a tripartite structure, including a N-terminal domain, a central NACHT domain, and C-terminal LRRs. A total of 22 human NLRs have been identified to date and they can be classified into four subfamilies based on their N-terminal effector domains. NLRA subfamily consists of one NLR member–CIITA, which possesses AT at its N-terminal region, while NLRB subfamily comprises NAIP that have BIR domains. NLRC subfamily members are characterised with the presence of CARD domain; NLRP subfamily members are PYD-containing NLRs and they are well-known for the regulation of NF-κB pathway to modulate the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines through the formation of the oligomeric inflammatory complex termed the “inflammasome”. (NLR, NOD-like receptor; NACHT, also known as NOD (nucleotide binding and oligomerisation domain); LRRs, leucine-rich repeats; AT, acidic transactivation domain; PYD, pyrin domain; CARD, caspase activation and recruitment domain; BIR, baculoviral inhibition of apoptosis protein repeat; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; FIND, function-to-find domain; X, unknown).