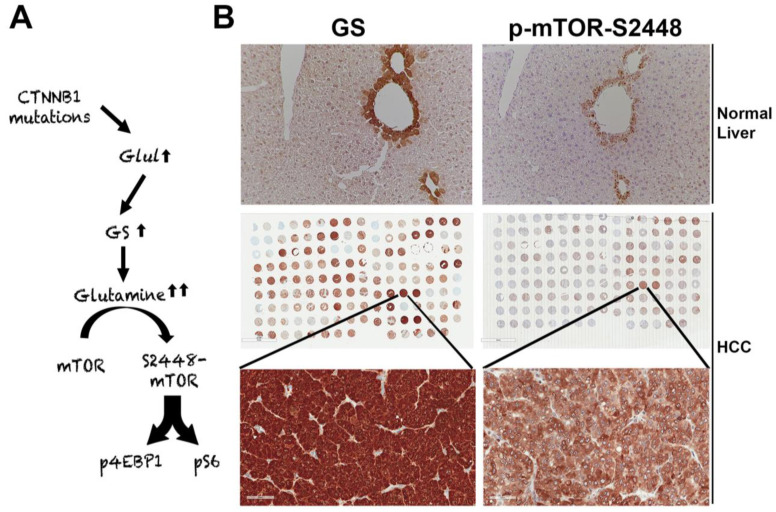
Figure 2.
Unique mTORC1 addiction of CTNNB1-mutated HCCs due to glutamine. (A) The unique axis of mTORC1 activation in β-catenin gene mutated HCCs due to overexpression of GLUL, the gene encoding for glutamine synthetase (GS), which generates glutamine from ammonia and glutamate, and in turn glutamine activates mTORC1 in lysosomes. (B) The top panel shows immunohistochemistry for GS and p-mTOR-S2448 in adjacent sections from a normal mouse liver. Both proteins are localizing exclusively to zone-3 hepatocytes in the immediate proximity to the central vein (200×). The whole slide scans (middle row) of two adjacent tissue microarrays of human HCC samples stained for the same antibodies against GS and p-mTOR-S2448 also shows several HCCs to be simultaneously positive for GS and p-mTOR-S2448. A representative tissue array sample is magnified (400×) to show GS and p-mTOR-S2448-positive HCC (bottom panels).