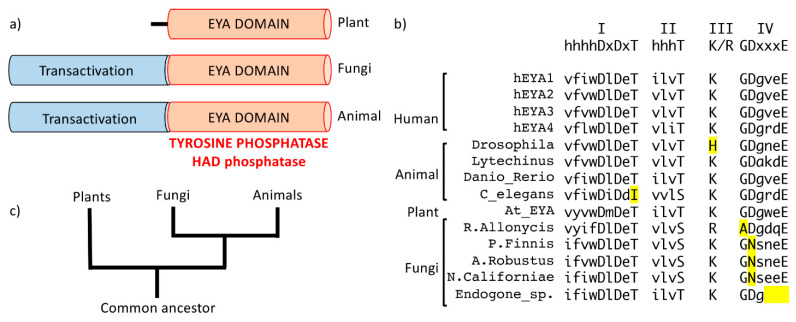
Figure 2.
(a) Domain architecture of eyes absent (EYA) proteins from plants, fungi, and animals showing the conserved EYA domain (ED) in orange and the variable N-terminal (transactivation) domain in blue. Plants do not have an N-terminal domain. (b) The characteristic haloacid dehalogenase (HAD) motifs in various animal, plant, and fungal species. There is complete conservation of the two Asp residues in Motif I. Non-conserved residues are highlighted in yellow. One fungal species does not have the complete Motif IV. (c) An evolutionary tree showing the likely parallel evolution of EYA in the three kingdoms: plant, animal, and fungi.