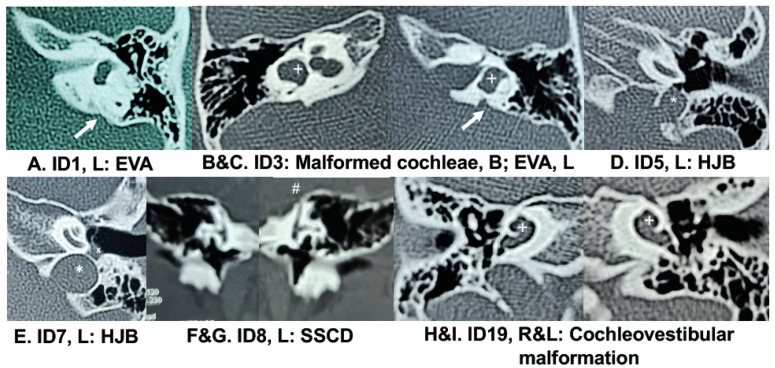
Figure 1.
Temporal bone images in six patients with hearing loss. (A) ID1 with the heterozygous DSPP c.730G>A (p.(Gly244Arg)) variant has enlarged vestibular aqueduct (EVA, arrow) on the left. (B,C) ID3 with the heterozygous LMX1A and COL2A1 variants has bilaterally malformed cochleae with incomplete cochlear turns (plus signs) and left-sided EVA (arrow). (D) ID5 with the heterozygous DMXL2 variant has a high jugular bulb (HJB, asterisk) on the left. (E) ID7 with the heterozygous MYO7A variant plus potentially compound heterozygous PCDH15 and CDH23 variants has HJB (asterisk) on the left. There is also fluid in the middle ear space (marked by X), indicating otitis media. (F,G) ID8 with the heterozygous COL11A1 and TECTA variants has left-sided superior semicircular canal dehiscence (SSCD, hash sign). (H,I) ID19 with the heterozygous MYO18B c.2555C>T (p.(Ala852)) variant has multiple congenital inner ear anomalies with bilaterally malformed cochleae, vestibules and semicircular canals (plus signs), as well as absence of the right cochlear and inferior vestibular nerves.