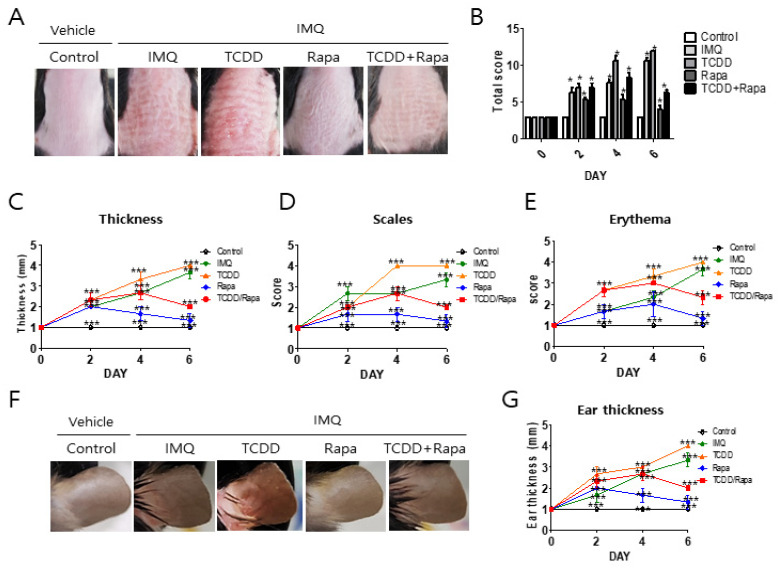
Figure 2.
The effects of TCDD, rapamycin, and cotreatment with both on the clinical severity of imiquimod-induced psoriatic mice. C57BL/6 mice were treated daily with vehicle control, IMQ, IMQ + TCDD, IMQ + Rapa, or IMQ + TCDD + Rapa applied on their shaved back skin and right ears (n = 5 per treatment group). (A) Macroscopic presentation of dorsal skin of mice from the 5 treatment regimens. (B) The severity of inflammation on the back was assessed using a scoring system similar to the human Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score. Thickness, scaling, and erythema of the back skin were scored “blindly” on a scale from 0 to 3 as follows: 0: none; 1: slight; 2: moderate; and 3: severe. (C–E) Detailed clinical disease score of thickness, scales, and erythema. Data represent mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s test. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001 compared with controls. (F) Macroscopic presentation of the right ear of mice from the 5 treatment regimens. (G) Assessment of ear skin thickness of the mice measured throughout the experiment. Statistical significance was determined by two-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s test. * p < 0.05; *** p < 0.001 compared with controls. IMQ: imiquimod, Rapa: rapamycin.