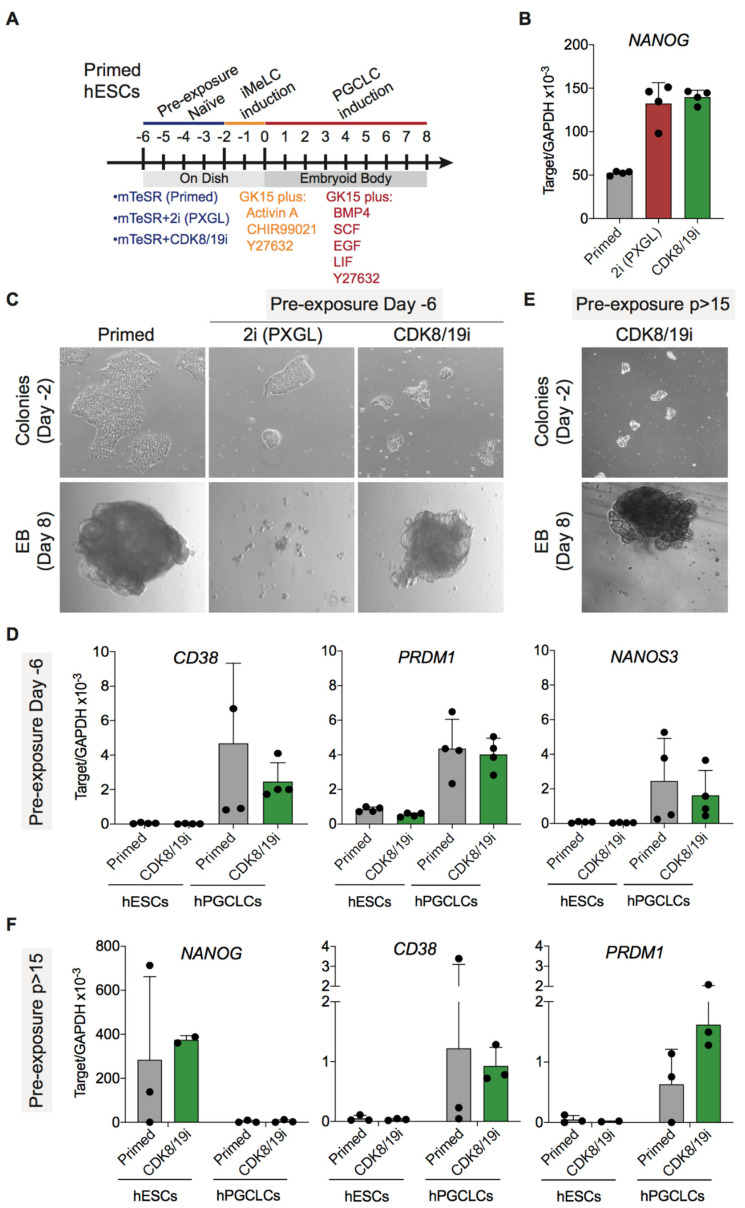
Figure 3.
CDK8/19i-naïve hPSCs can differentiate into primordial germ cell-like cells (hPGCLCs). (A) Experimental scheme for assessing PGC differentiation of primed, 2i (PXGL) and CDK8/19i-naïve hESCs. iMeLCs: induced mesoderm-like cells. (B) mRNA expression level of NANOG assessed by qRT-PCR. Up-regulation of NANOG is a feature of the naïve state. Data represent mean ± Std Dev from 4 technical replicates. (C) Brightfield images showing H1 hESCs before and after exposure to naïve conditions and embryoid bodies (EBs) in hPGCLCs induction conditions at day 8. (D) mRNA expression level of selected hPGCLC markers in hESCs and EBs differentiated into hPGCLCs assessed by qRT-PCR. Data of hESC are mean ± Std Dev from 4 technical replicates and data of hPGCLCs are mean ± Std Dev from 4 biological replicates. (E) Brightfield images showing H1 hESCs cultured in the presence of CDK8/19i for more than 15 passages (p > 15). Lower panel shows EB formation under PGCLC differentiation conditions at day 8. (F) mRNA expression level of pluripotency marker NANOG and selected hPGCLC markers in H1 cells primed or long-term cultured in CDK8/19i (more than 15 passages) before or after differentiation into hPGCLCs assessed by qRT-PCR. Data are mean ± Std Dev from 3 biological replicates.