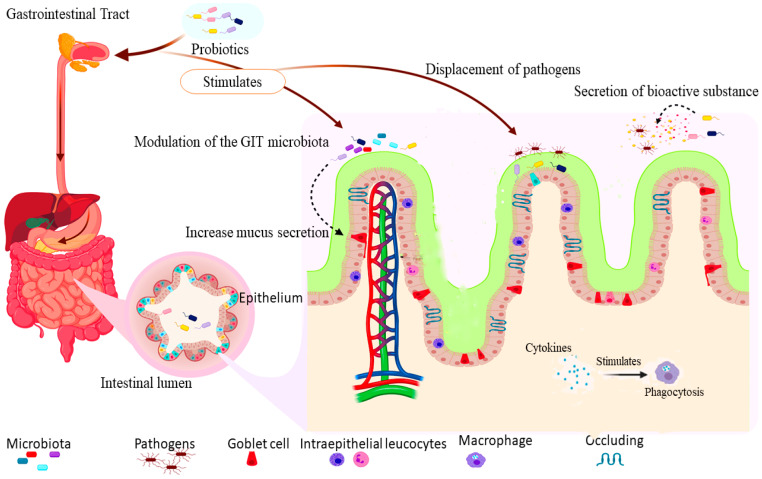
Figure 1.
(created with BioRender; https://app.biorender.com/illustrations/edit/6001622bd73fad00a4e81c08, accessed on 28 November 2020) shows the mechanism of actions of probiotics: the intake of probiotics stimulates an increase in the secretion of mucus by goblet cells, mobilization of intraepithelial leucocytes, and tightening of the tight junctions to protect against the invasion of pathogens. The increase in mucus secretion and improvement of gut microbiota enhances competitive displacement and inhibition of pathogens adhesion to the gut epithelial surface. Furthermore, the action of bioactive substances such as lysozyme and cytokines stimulate phagocytosis by macrophages.