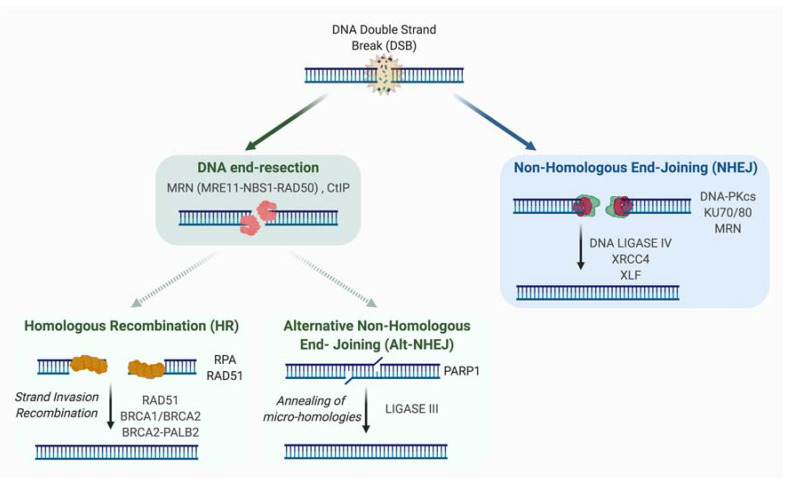
Figure 1.
Double-Strand Break Repair Mechanisms. A deficient repair of DSB has detrimental consequences, including genomic instability and cell death. There are two main mechanisms to repair DSBs: HR and canonical NHEJ (C-NHEJ). A pivotal process in the choice of DNA repair pathways is the DNA end-resection. Indeed, if DNA end-resection is blocked, C-NHEJ is favored to the detriment of HR. C-NHEJ involves the ligation of DNA extremities without the requirement for homology and does not require resection. An alternative pathway of NHEJ (Alt-NHEJ) exists and unlike C-NHEJ, it is highly inaccurate and requires short DNA end-resection. Unlike Alt-NHEJ, HR requires extensive DNA end-resection and requires the presence of an intact homologous template.