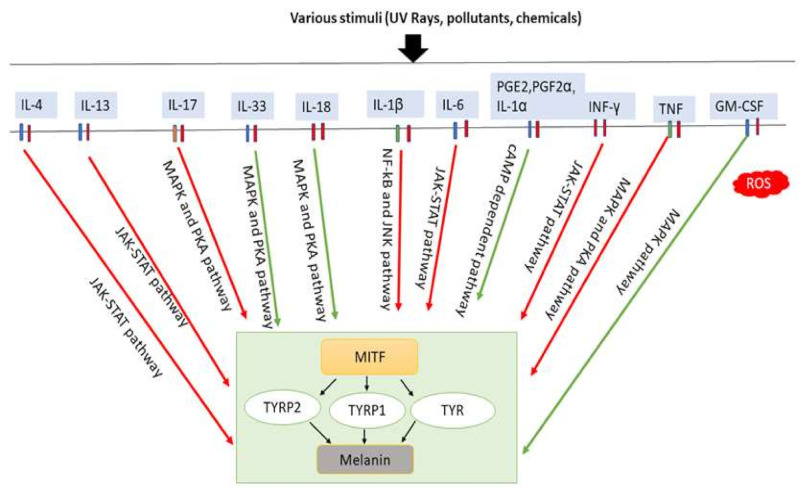
Figure 4.
Involvement of inflammatory factors in melanogenesis. Inflammatory factors including IL-33, IL-18, and GM-CSF promote melanogenesis by stimulating the MAPK and PKA pathways either simultaneously or individually. In addition, PGE2, PGF2α, and IL-1α promote melanogenesis by stimulating cAMP-dependent pathway. In contrast, inflammatory factors such as IL-4, IL-13, IL-6, IL-17, IL-1β, TNF and IFN-γ inhibit melanogenesis by suppressing the PKA and MAPK, or JAK-STAT, or NF-κβ and JNK pathways. IL-33: interleukin-33; IL-18: interleukin-18; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; PGF2α: prostaglandin F2α; IL-1α: interleukin-1α; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; IL-4: interleukin-4; IL-13: interleukin-13; IL-6: interleukin-6; IL-17: interleukin-17; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IFN-γ: interferons-γ; PKA: protein kinase A; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinases; JAK-STAT: Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription; NF-κβ: nuclear factor kappa-B; TYR: tyrosinase; TRRP1: tyrosinase-related protein-1; TRRP2: tyrosinase-related protein-2. Red arrows indicates inhibition; green arrows indicate promotion.