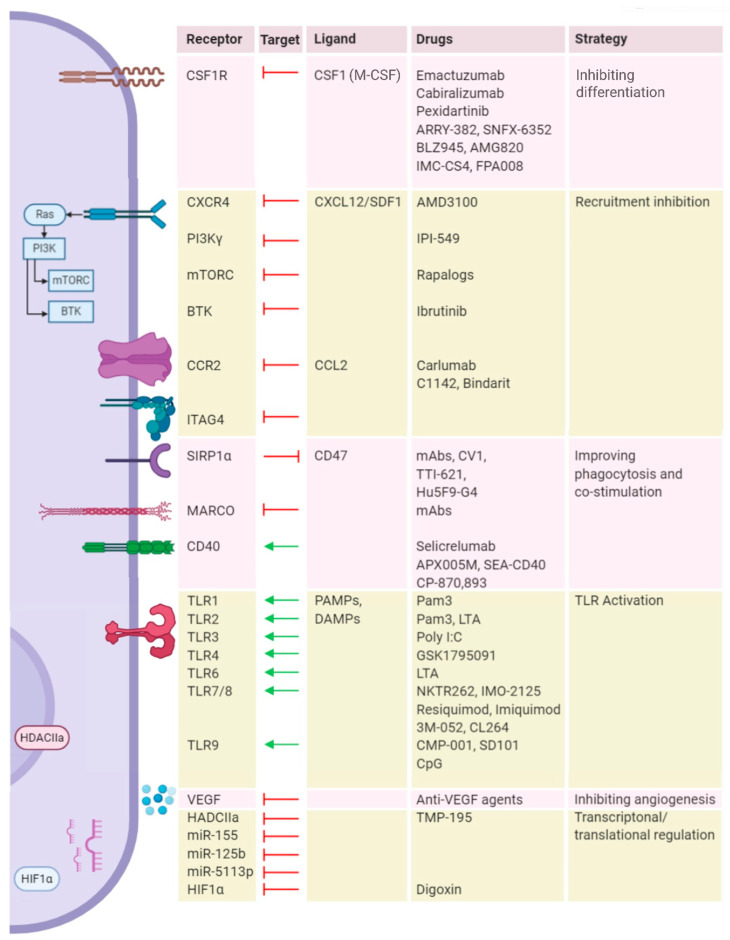
Figure 3.
Current landscape of macrophage repolarization strategies. Various receptors, secretory molecules and regulatory pathways that skew macrophages to M2 state are lined on the left, and the respective therapeutic targets, their ligands, targeting strategies, and therapeutic agents are listed in the corresponding table on the right. Abbreviations: CSF1R: Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor; CSF1: Colony-stimulating factor 1; M-CSF: Macrophage colony-stimulating factor; CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; CXCL12: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; SDF1: stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF1); PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; mTORC: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex; BTK: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; CCR2: C-C chemokine receptor type 2; CCL2: C-C Motif chemokine ligand 2; ITAG: Integrin alpha gamma; SIRP1α: signal regulatory protein alpha; MARCO: Macrophage receptor with collagenous structure; TLR: Toll-like receptor; CD: Cluster of differentiation; PAMPs: Pathogen-activated molecular patterns; DAMPs: Damage-associated molecular patterns; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HDACIIa: Histone deacetylase class IIa; HIF1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha.