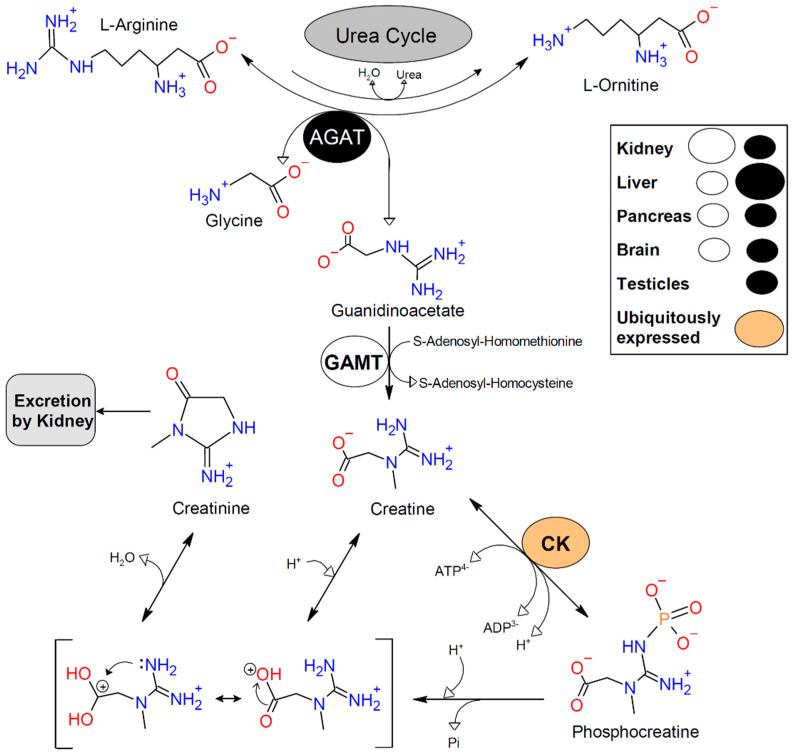
Figure 1.
Creatine synthesis/excretion and the creatine kinase reaction. Enzymes are represented by ovals. Once synthesized from L-arginine, glycine, and S-adenosyl-L-methionine, creatine (Cr) is converted to phosphocreatine (PCr) by means of the creatine kinase (CK), which catalyzes the reversible transference of a phosphoryl group (PO32−), not a phosphate (PO43−), from ATP. The kinetic rate of the non-enzymatic conversion of Cr (or PCr) to creatinine (Crn) depends on the H+ concentration of the media. It is important to note that neither Crn nor PCr are substrates of the sodium- and chloride-dependent creatine transporter (not shown). Oval size represents the expression level of AGAT (black), GAMT (white), and CK (orange) in some tissues. For more details related to expression in different tissues or conditions (i.e., pathologies) use the following BioGPS ID numbers: AGAT–2628; GAMT–2593. AGAT: L-Arginine-Glycine amidinotransferase; GAMT: Guanidinoacetate N-Methyltransferase; H+: hydrogen ion; Pi: inorganic phosphate. Modified with permission from Bonilla and Moreno [7] using the Freeware ACD/ChemSketch 2021 (Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada).