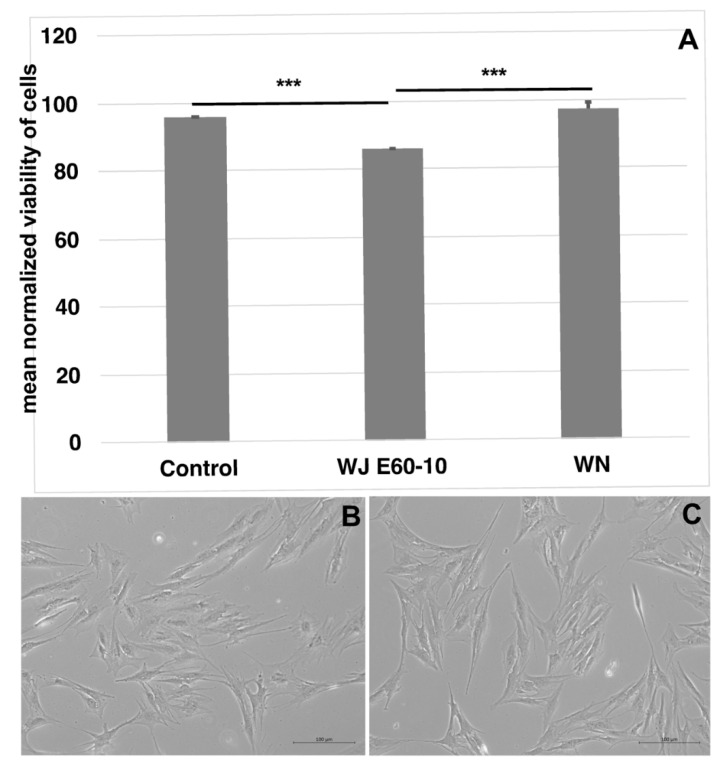
Figure 1.
Viability assessment of cells after WN and WJ injections in capture fluid. Cells were injected by WJ in capture fluid (n = 12), collected, and counted by trypan exclusion to determine the viability. WJ injection reduced the viability of pADSCs significantly compared to cells injected through a standard 22G cannula (n = 4) or by WN (n = 10) (A). Microscopic differences in cell morphology or proliferation were not observed between the 22G cannula (B) and the WJ-injected pADSCs (C). *** p < 0.001. Abbreviations: WJ—waterjet, WN—Williams needle.