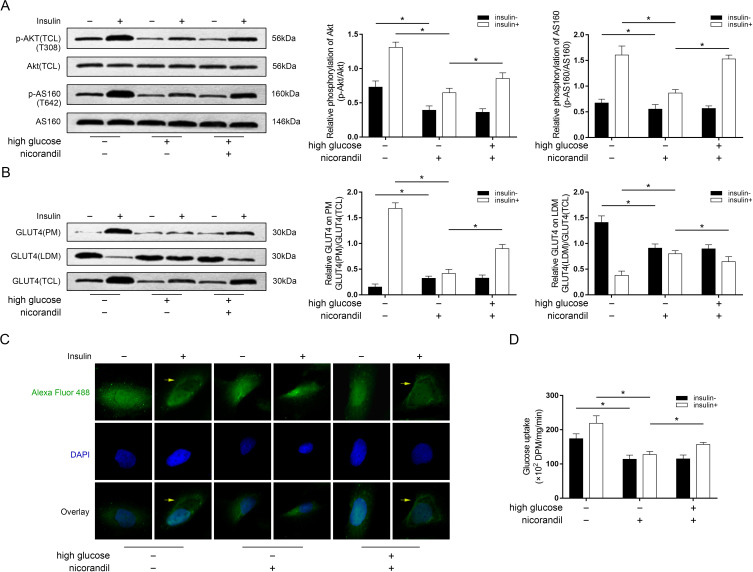
Figure 4.
Effects of nicorandil on glucose uptake and Akt phosphorylation-mediated glucose transporter (GLUT)4 translocation in high-glucose incubated L6 cells. (A) Immunoblots of phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), Akt, phosphorylated AS160 (p-AS160) and Akt substrate 160 kDa (AS160). Columns indicated the relative phosphorylation levels of Akt and AS160 in L6 cells from each group received insulin stimulation (insulin+) and did not receive insulin stimulation (insulin−), respectively. (B) Immunoblots of GLUT4 in plasma membrane fractions (PM), low-density microsomes fractions (LDM) and total cell lysate (TCL) in L6 cells from each group. Columns indicated relative expression levels of GLUT4 on PM and LDM in L6 cells from each group received insulin stimulation (insulin+) and did not receive insulin stimulation (insulin−), respectively. (C) Representative fluorescent images of GLUT4 (stained by Alexa Fluor 488), 2-(4-amidinophenyl)-6-indolecarbamidine dihydrochloride (DAPI) and their overlay were demonstrated. Yellow arrows were pointing at accumulated Alexa Fluor 488 (indicating GLUT4) on PM. (D) Columns indicated the detected glucose uptake of cultured L6 cells from each group received insulin stimulation (insulin+) and did not receive insulin stimulation (insulin−), respectively. *P<0.05.