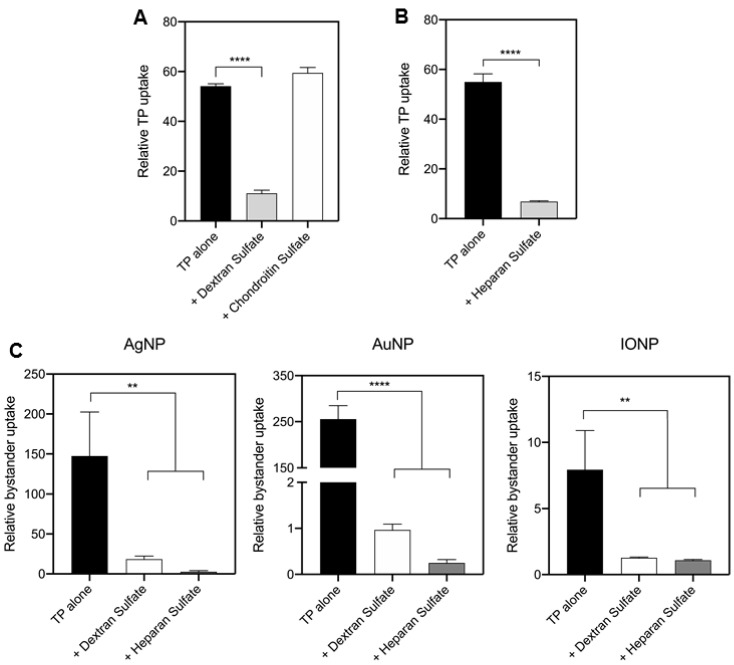
Figure 3.
Receptor dependence. (A) Blockage of TP uptake by a scavenger receptor inhibitor. CHO cells were incubated with 5 μg/mL dextran sulfate or chondroitin sulfate together with TP peptide for 1 h, as described in the Methods. Cells were then washed, detached and subjected to flow cytometry. Fluorescence intensity of internalized TP peptide was normalized to that of cells alone (y-axis). Error bars, mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) (n = 3). Two tailed Student’s t-test was performed. **** p < 0.0001 in comparison with the TP alone group. (B) Blockage of TP uptake by heparan sulfate inhibition. CHO cells were incubated with 1000 μg/mL soluble heparin together with TP peptide for 1 h, as described in the Methods. Flow cytometry was used to quantify the fluorescence intensity of internalized TP peptide which was further normalized to that of cells alone (y-axis). Error bars, mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) (n = 3). Two tailed Student’s t-test was performed. **** p < 0.0001 in comparison with the TP alone group. (C) Blockage of NP bystander uptake by heparan sulfate and a scavenger receptor inhibitor. As described in the Methods, CHO cells were incubated with indicated bystander NPs (AgNPs, AuNPs and IONPs) + TP peptide alone, or together with dextran sulfate or heparan sulfate. Fluorescence intensity of bystander NPs per sample was quantified by flow cytometry and normalized to that of cells with bystander NPs alone (y-axis). Data were presented as mean ± s.d. (n = 3) and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.0001 in comparison with the TP alone group.