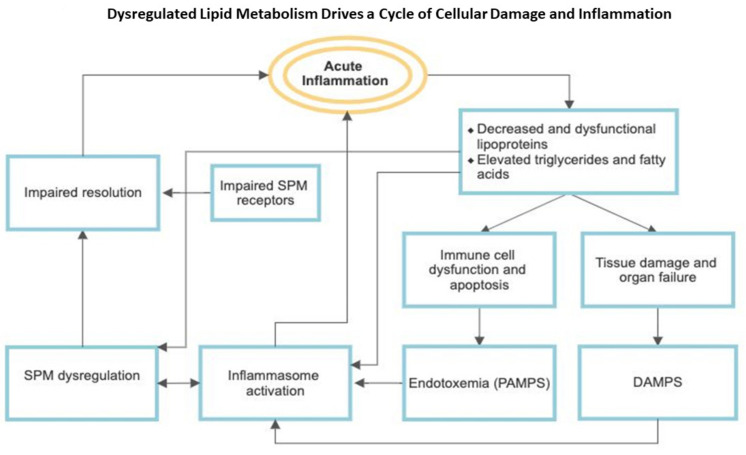
Figure 2.
Dysfunctional HDL (Dys HDL) fails to regulate and actively impairs the innate immune response (see Figure 1). Elevations in triglycerides and fatty acids, which have innate signaling properties contribute to this impairment. This leads to tissue damage, organ failure, and immune cell dysfunction. These factors contribute to complex interactions between sustained inflammasome activation and dysregulated lipid pro-resolving mediators, maintained by low grade endotoxemia and DAMPs, leading to an inappropriate inflammatory response. SPMs, specialized pro-resolving mediators; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns.