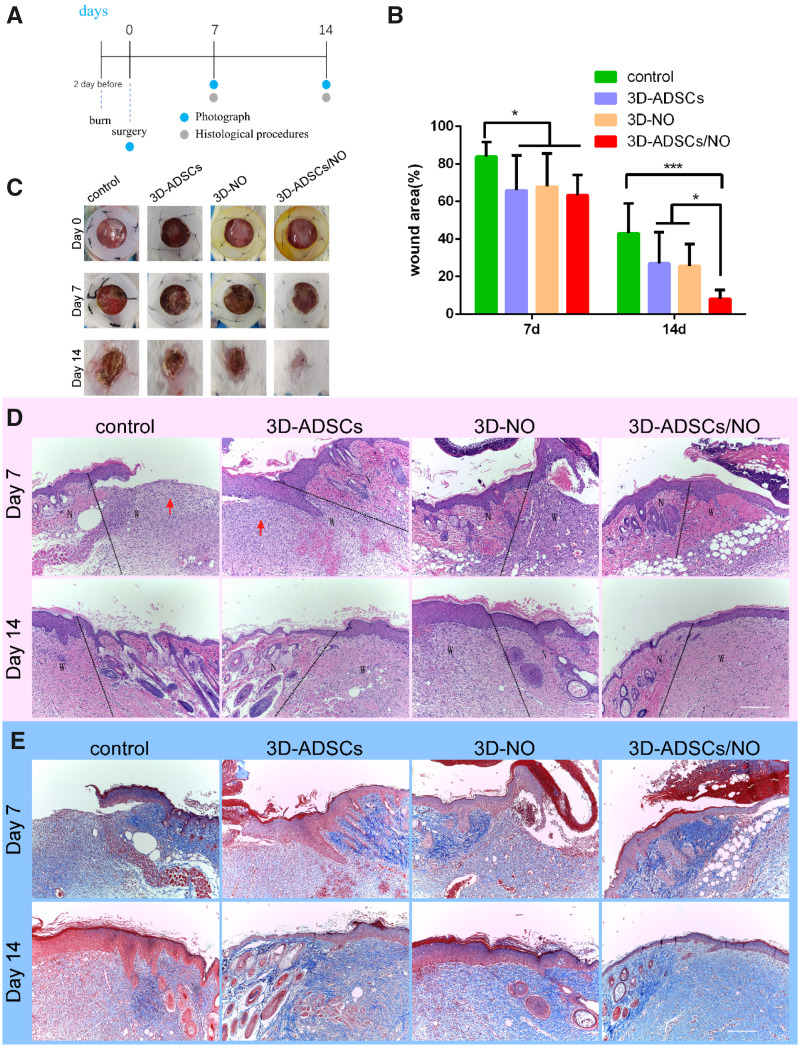
Figure 4.
(A) Burn wounds were made 2 days before and the necrotic skin was removed at Day 0. Mice were randomized into four groups (n = 8 each group) according to different treatments after surgery: control group, 3D-ADSCs, 3D-NO and 3D-ADSCs/NO. Photograph of the wound area was performed at Days 0, 7 and 14, and mice were sacrificed to have IHC procedure at Days 7 and 14. (B) Quantification of wound area expressed as the percentage of the initial wound size. Wound closure can be observed at Day 14 which the 3D-ADSCs/NO group presented the most remarkable effect of wound healing. (C) Representative images of the mouse burn wound healing process with different treatments over 14 days. (D) HE-stained images of mouse burn wound skin with different treatments. Wounds treated with 3D-ADSCs/NO presented more complete skin structures. The red arrows indicate the severe inflammatory cell infiltration into the wound bed. ‘N’ is represented for normal skin and ‘w’ is represented for wound area. (E) MT-stained images of mouse burn wound skin with different treatments. At Days 7 and 14, the expression of collagen in wound tissue was increased in the 3D-ADSCs/NO group compared with others (*P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001; scale bar: 200 μm).