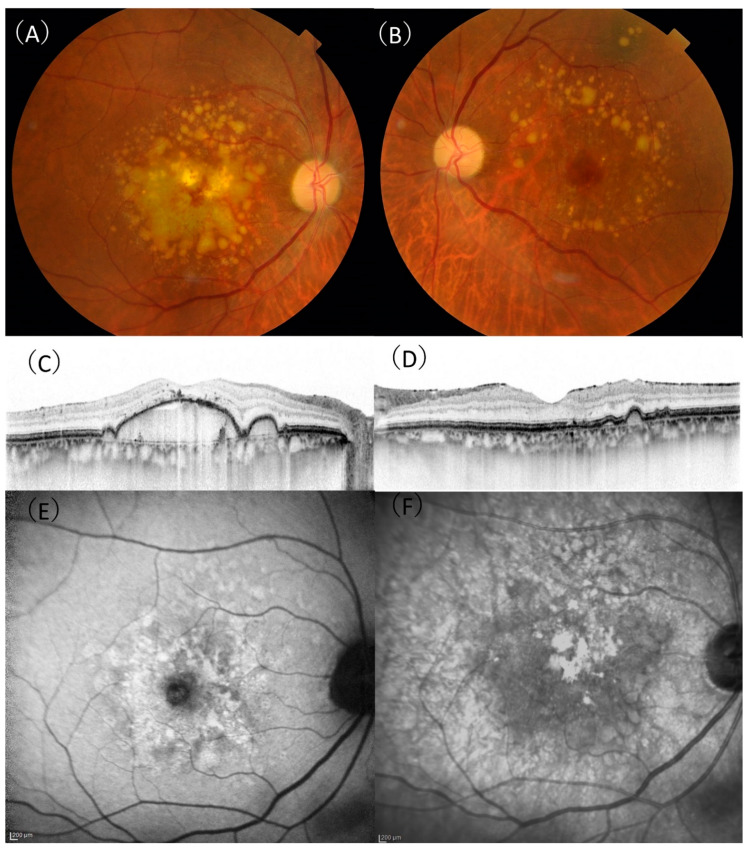
Figure 1.
A 75-year-old male patient with drusenoid pigment epithelial detachment. (A) In the right eye, aggregation of confluent drusen was observed in the macula. (B) The aggregation of drusen in the left eye was spared from the central macula. (C) A horizontal optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan showing a large drusenoid pigment epithelial detachment with 307 µm height and 3943 µm width in the right eye. (D) A horizontal OCT scan showing retinal pigment elevation corresponding to a druse in the left eye. (E) There were no characteristic signs of reticular pseudodrusen on fundus autofluorescence. (F) There were no characteristic signs of reticular pseudodrusen on near-infrared reflectance.