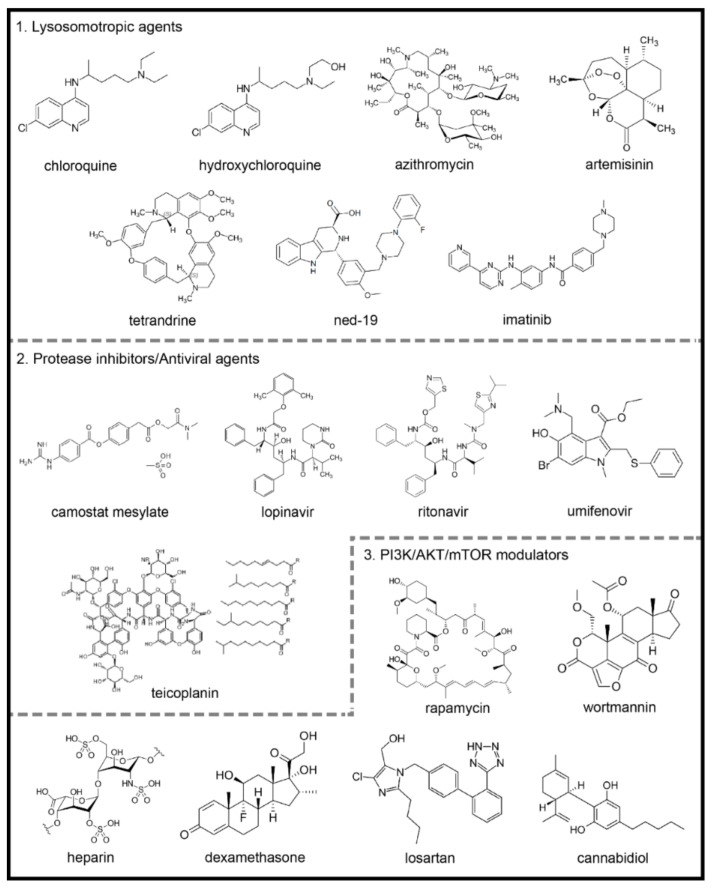
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of potential autophagy-related drugs for SARS-CoV-2 infection. The drugs were divided in three groups according to their effects on the autophagy signaling pathway and possible effect against SARS-CoV-2 infection. The lysosomotropic agents (1) can prevent coronavirus infection by alkalinizing the acid pH in the endolysosomal system; some examples are chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, artemisinin, two-pore channel antagonists (such as tetrandrine and ned-19) and imatinib. The protease inhibitors/antiviral agents (2) can inhibit the proteolytic cleavage of the spike coronavirus protein, which is necessary for viral entry into host cells; some examples are camostat mesylate, lopinavir, ritonavir, umifenovir and teicoplanin. The third group is composed by PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways modulators (3), which can modulate intracellular pathways related to autophagy and coronavirus infection; some examples are the rapamycin, wortmannin, the anticoagulant heparin, the glucocorticoid dexamethasone, losartan and cannabidiol. The figures for each chemical structure are from according to Wikimedia Commons (Public Domain).