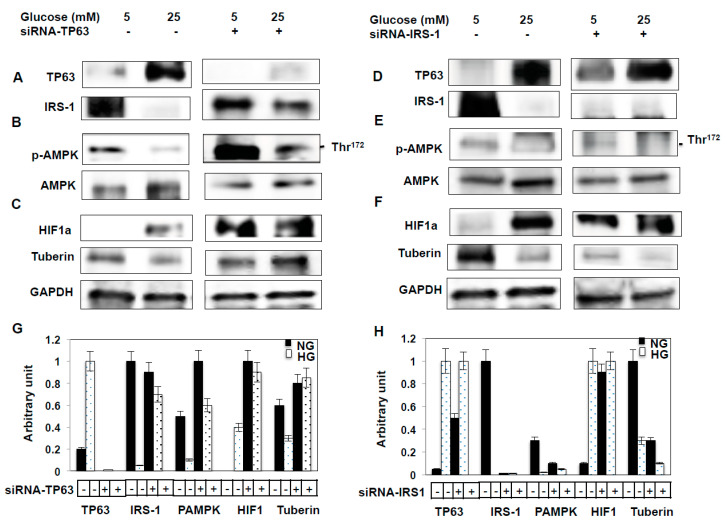
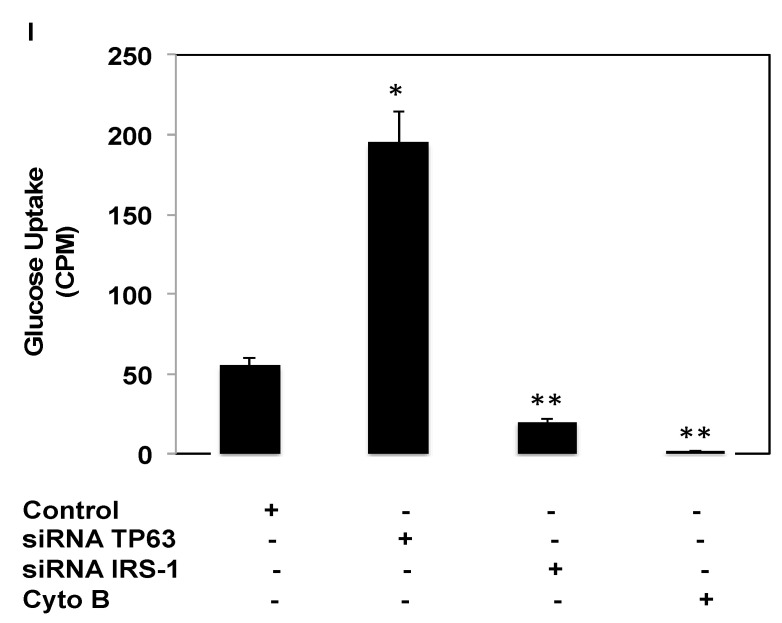
Figure 3.
The downregulation of TP63 increases IRS-1, resulting in increased glucose uptake. Mouse tubular (MCT) cells were transfected with siRNA against TP63 or IRS-1 in normal glucose (NG) and high glucose (HG) conditions. (A) TP63 is downregulated significantly by TP63 siRNA in both NG and HG. The downregulation of TP63 increased the expression of IRS-1 significantly. (B) Both p-AMPK and AMPK were increased significantly by downregulating TP63 in both NG and HG compared to non-transfected cells. (C) HIF1a is significantly increased in HG-treated cells, while the downregulation of TP63 resulted in decreased expression of HIF1a. (D) The downregulation of IRS-1 by siRNA-IRS-1 in NG and HG resulted in a significant increase in TP63 expression under NG and HG conditions. (E) The downregulation of IRS-1 decreased p-AMPK significantly compared to non-transfected cells. (F) HIF1a was significantly increased with the downregulation of IRS-1, while tuberin expression was decreased under both NG and HG conditions. (G,H) Histogram of average expression of each protein presented as an arbitrary unit was calculated from each protein and normalized by Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) from 2 Western blots. (I) Glucose uptake (CPM) is increased by inhibiting TP63 and decreased by inhibiting IRS-1. Cells were transfected either with siRNA-TP63 or siRNA-IRS-1, resulting in an increase and decrease in glucose uptake compared to the non-transfected cells (control), respectively. Cells treated with glucose transport inhibitor cytochalasin B resulted in complete inhibition of glucose transport. Data presented as means ± SE (n = 6). A significant difference from non-transfected cells is indicated by * p < 0.01 and from cells transfected with siRNA-IRS-1 or treated with cytochalasin B groups by ** p < 0.001.