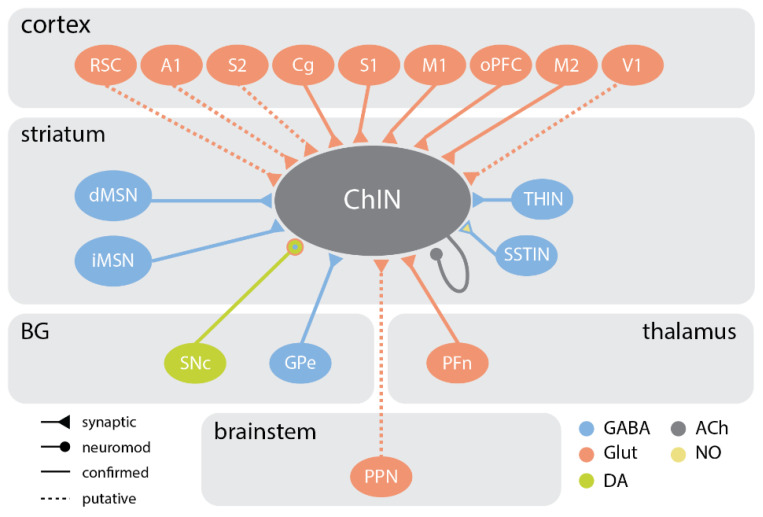
Figure 2.
Schematic of major inputs to striatal cholinergic interneurons. Cortical inputs to cholinergic interneurons (ChINs) include the cingulate cortex (Cg), orbital prefrontal cortex (oPFC), primary somatosensory (S1) and motor (M1) cortices, and secondary motor cortex (M2). Putative cortical inputs to ChINs include the secondary somatosensory cortex (S2), primary visual (V1) and auditory (A1) cortices, and the retrosplenial cortex (RSC). Other extrastriatal inputs to ChINs include basal ganglia (BG) structures substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) and external globus pallidus (GPe), the parafascicular thalamic nucleus (PFn), and the brainstem pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN). Intra-striatal inputs to ChINs include medium spiny neurons (MSN), tyrosine hydroxylase-expressing interneurons (THIN), somatostatin-expressing interneurons (SSTINs; or LTSI), and ChIN automodulation. Note: connections shown based on neuroanatomical tracing and optogenetic mapping studies [89,95].