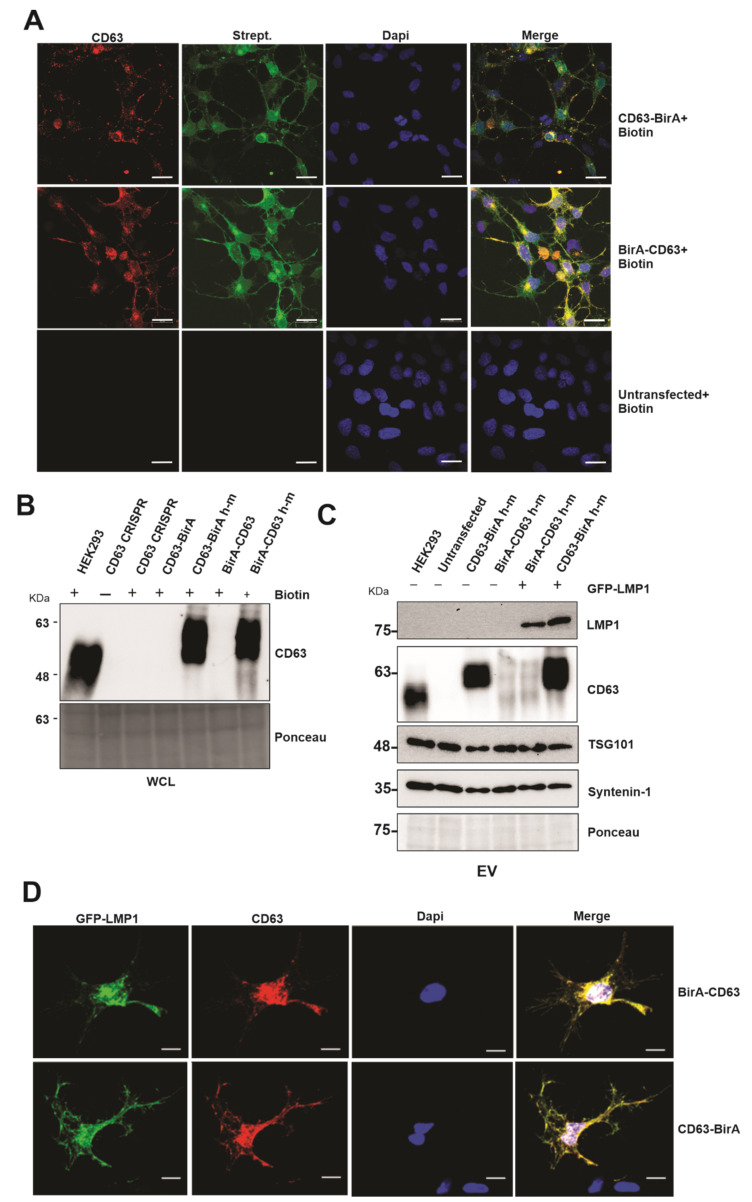
Figure 1.
Expression of CD63-BioID constructs and validation of CD63-dependent exosome targeting of LMP1. CD63-BirA human constructs were mutated to mouse in the guide DNA sequence and expressed in HEK293 cells with CD63 CRISPR background. Human to mouse (h–m) mutations in the guide target sequence allowed successful translation of over-expressed constructs. (A) Co-localization of CD63 and biotinylated proteins: double immunofluorescence staining of CD63 and Alexa-488 conjugated streptavidin. Co-localization indicates CD63-BirA biotinylated proximal and interacting proteins. (B) Western blot analysis using anti-CD63 antibody showed successful expression of CD63 in HEK293 CRISPR cells. (C) EVs purified from the supernatant of CD63 CRISPR or cells expressing BirA-CD63 or CD63-BirA with or without GFP-LMP1 were purified using the ultra-centrifugation method and were used for Western blot. The results indicate that CD63 h-m mutant constructs can mediate exosome targeting of LMP1. (D) Immunofluorescence staining using anti-CD63 and anti-GFP antibodies using the cells expressing CD63 BioID h-m and GFP-LMP1. Co-localization indicates CD63 h-m mutants can interact with LMP1. WCL: whole cell lysate. Scale bar: 20 µm.