Table 5.
Acidic hydrolysis of cotton fiber. In each process, 100 g of comminuted cotton yarn (>0.5 cm long) and 2 dm3 of the solution of H2SO4 (concentration 2–10%) were used. The process was carried out between 1 and 4 h in a temperature range of 80–160 °C.
| No | Time [h] |
C H2SO4 [%] |
Temp. [oC] |
Dry Mass of Solid Residue [g] | CGlucose
HPLC [mol/dm3] |
Cellulose Crystallinity of the Solid Residue [%] |
Product of Cotton Hydrolysis GC-MS Analysis (R.Time) |
SEM Images (×500 Magnification) of the Fibers after Hydrolysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
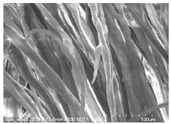
| 1 | 2 | 0 | 120 | 92.2 | 0 | 91 | - |
|
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 120 | 86.9 | 0.008 | 89 | - |

|
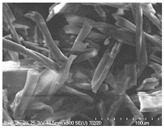
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 120 | 81.4 | 0.010 | 95 | (4.970) Furfural (8.558) 2-Furanocarboxaldehyde, 5-methyl- |
|
| 4 | 4 | 2 | 120 | 82.8 | 0.015 | 99 | - |

|
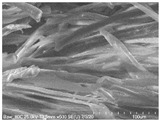
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 80 | 91.5 | 0 | 90 | - |
|
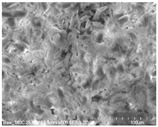
| 6 | 2 | 2 | 160 | 42.9 | 0.020 | 99 | (4.943) Furfural (7.885) 2(5H)-Furanone, 5-methyl- (8.520) 2-Furanocarboxaldehyde, 5-methyl- (12.438) Levulinic acid |
|
| 7 | 2 | 5 | 120 | 81.9 | 0.018 | 99 | - |
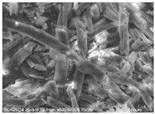
|
| 8 | 2 | 10 | 120 | 84.7 | 0.018 | 99 | - |
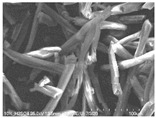
|
