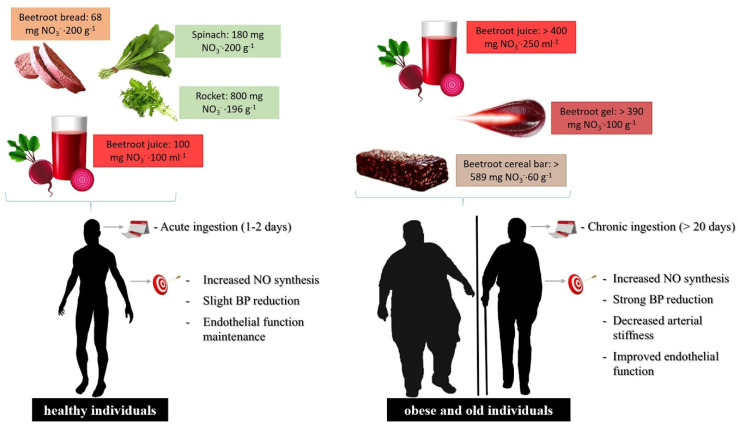
Figure 2.
Food formulations and supplementation regimen of dietary NO3− in healthy or cardiovascular-compromised patients. For individuals presenting risk factors for the development of cardiovascular disease, the dietary NO3− dose should be higher to promote the systemic elevation of plasma NO3− and NO2− levels compared to healthy individuals, increasing NO generation by the NO3−/NO2− pathway, where increased levels must be administered through chronic and uninterrupted supplementation.