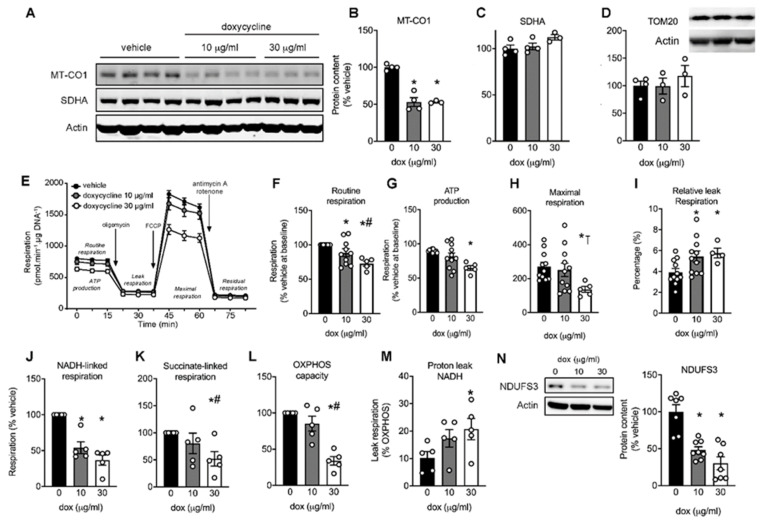
Figure 1.
Mito-nuclear protein imbalance and mitochondrial complex I dysfunction in H9C2 cardiomyoblasts exposed to doxycycline. H9C2 cardiomyoblasts were exposed to doxycycline at 0, 10 or 30 μg/mL for 72–96 h. (A) Western blot showing protein expression of mitochondrially-encoded cytochrome c oxidase I (MT-CO1) and nuclear-encoded succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit A (SDHA). Actin was used as a loading control. (B) MT-CO1 protein content (normalized to vehicle) was significantly lower in doxycycline-treated cells. (C,D) SDHA and TOM20 protein content is unaffected by doxycycline. (E) Typical Seahorse run with injections of oligomycin, carbonylcyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)-phenylhydrazone (FCCP), antimycin A and rotenone highlighted. (F–H) Routine, oxygen consumption used for ATP production (Routine-Leak respiration) and maximal respiration was reduced in doxycycline-treated cells. (I) Normalized leak respiration (i.e., Leak / Maximal respiration) was higher in both concentrations of doxycycline. (J) Mitochondrial complex I-stimulated respiration (with substrates pyruvate and malate) was significantly reduced in cells exposed to 10 or 30 µg/mL doxycycline compared to vehicle. (K) Complex II-stimulated (with succinate and rotenone) was only reduced at 30 µg/mL doxycycline compared to vehicle or low dose doxycycline. (L) Oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) capacity (with pyruvate, malate and succinate) dose-dependently decreased following doxycycline exposure, note that panel H shows maximal uncoupled respiration. (M) Relative leak respiration (after oligomycin) with complex I substrates showed increased proton leak from complex I at 30 µg/mL doxycycline. No differences were observed with other substrates. (N) Western blot analysis revealed a large reduction in protein content of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial complex I subunit NDUFS3 in doxycycline-treated H9C2 cells. Bar graphs are expressed as mean±SEM. *: p < 0.05 vs. vehicle, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test for multiple comparisons, #: p < 0.05 vs. 10 µg/mL doxycycline. ⊺: p = 0.088 vs. 10 µg/mL doxycycline.