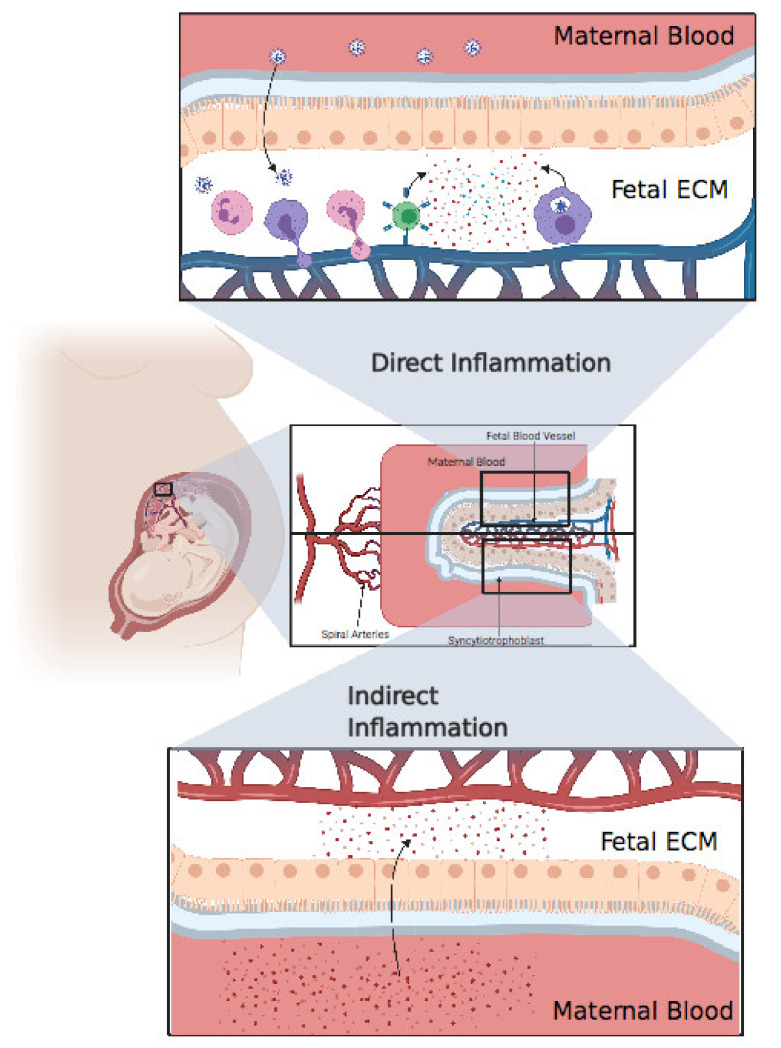
Figure 3.
Direct inflammation or indirect inflammation. Direct inflammation: after viral invasion of the placenta, fetal immune cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells, extravasate from fetal blood to the placental extracellular matter, resulting in an extensive inflammatory response in the fetal extracellular matrix (ECM). Finally, these inflammatory cytokines pass through the blood, resulting in systemic inflammation in the fetus. Indirect inflammation: inflammatory cytokines circulating in maternal blood after a cytokine storm might pass through the placenta, resulting in indirect inflammation. Created with BioRender.com.