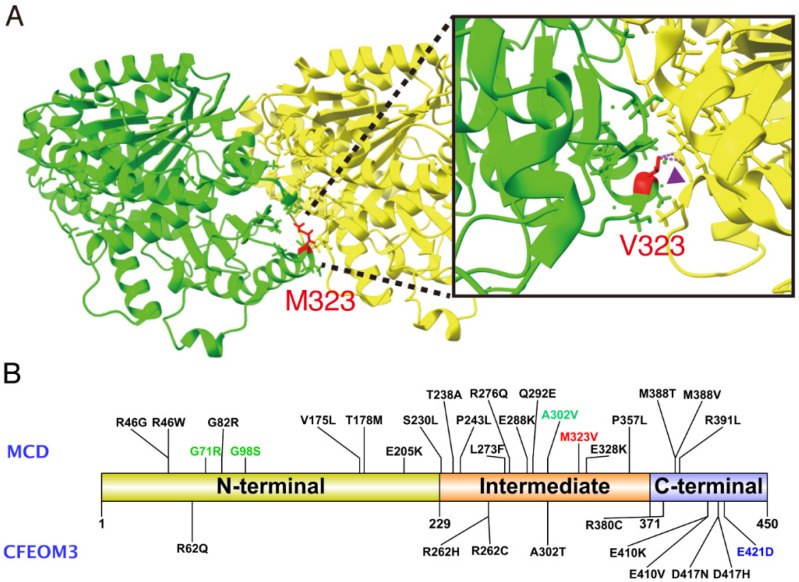
Figure 3.
(A) A protein model with UCSF ChimeraX, showing the unstable formation of αβ tubulin heterodimer in M323V syndrome. Green, class III β-tubulin encoded by TUBB3; Yellow, α tubulin encoded by TUB1A1. A clash occurred between TUBB3:p.V323 and TUBA1A:p.Y210 (arrowhead). (B) Schematic diagram of deleterious variants in TUBB3 functional domains. A total of thirty-two missense variants, including p.M323V, have been reported until recently. Variants associated with malformations of cortical development (MCD) with or without congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles type 3 (CFEOM3) are marked above, and variants only representing CFEOM3 are marked at the bottom. Most variants in the N-terminal and the intermediate domain cause MCD, and missense variants in the C-terminal cause either MCD or CFEOM3 phenotypes. A red word indicates the variant in this study. Green words denote previously reported variants associated with infantile nystagmus, and a blue word indicates a variant associated with monocular elevation deficiency.