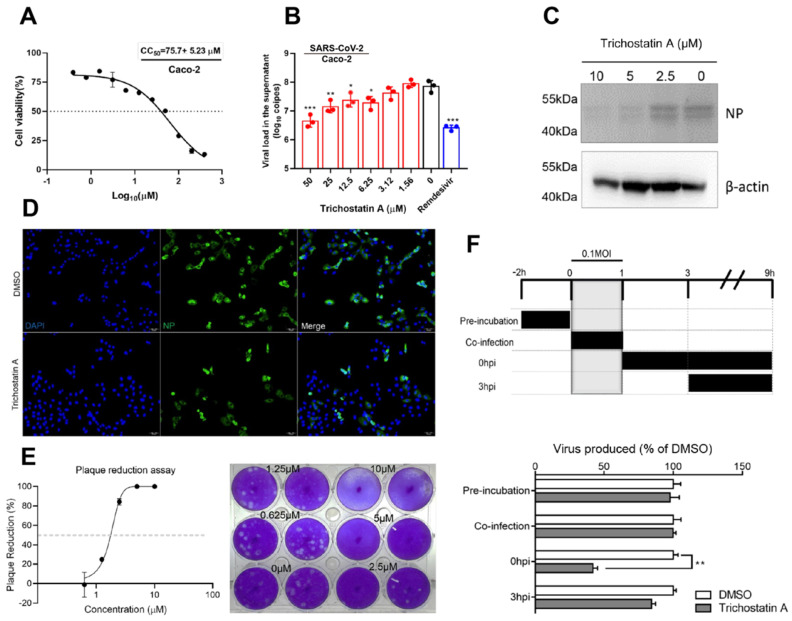
Figure 3.
Antiviral activity of trichostatin A against SARS-CoV-2. (A) Cytotoxicity of trichostatin A in Caco-2 cells as determined by measuring the cellular ATP activity (CellTiter-Glo assay, 48h post drug treatment). (B) Multi-cycle virus growth assay in the presence or absence of trichostatin A. Caco-2 cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI=0.01). Viral titers in cell culture supernatants were quantified by quantitative RT-PCR assay at 48hpi. Groups were analysed by One-way ANOVA when compared with the non-treated group (0µM). Remdesivir was included as a positive control. (C) Western blot showed reduced SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein production after trichostatin A treatment. Caco-2 cells with different treatments as indicated were infected with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI=0.1) and lysed at 24hpi. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein protein (green) and cell nucleus (blue). Fixation and staining were performed after trichostatin A (10µM) was used to treat SARS-CoV-2-infected (MOI=0.1) VeroE6 cells for 24h. (E) Plaque reduction assay showing the dose-dependent live SARS-CoV-2 reduction after trichostatin A treatment on VeroE6 cells. (F) Time-of-drug-addition assay. The upper panel depicts the scheme of experimental design; lower panel shows the viral titer collected in the cell culture supernatant and normalized by DMSO as a control. The experiments were performed in triplicate and replicated twice. The results are shown as mean± SD. * indicated P<0.05 and ** indicated P<0.01 (Student's t-test).