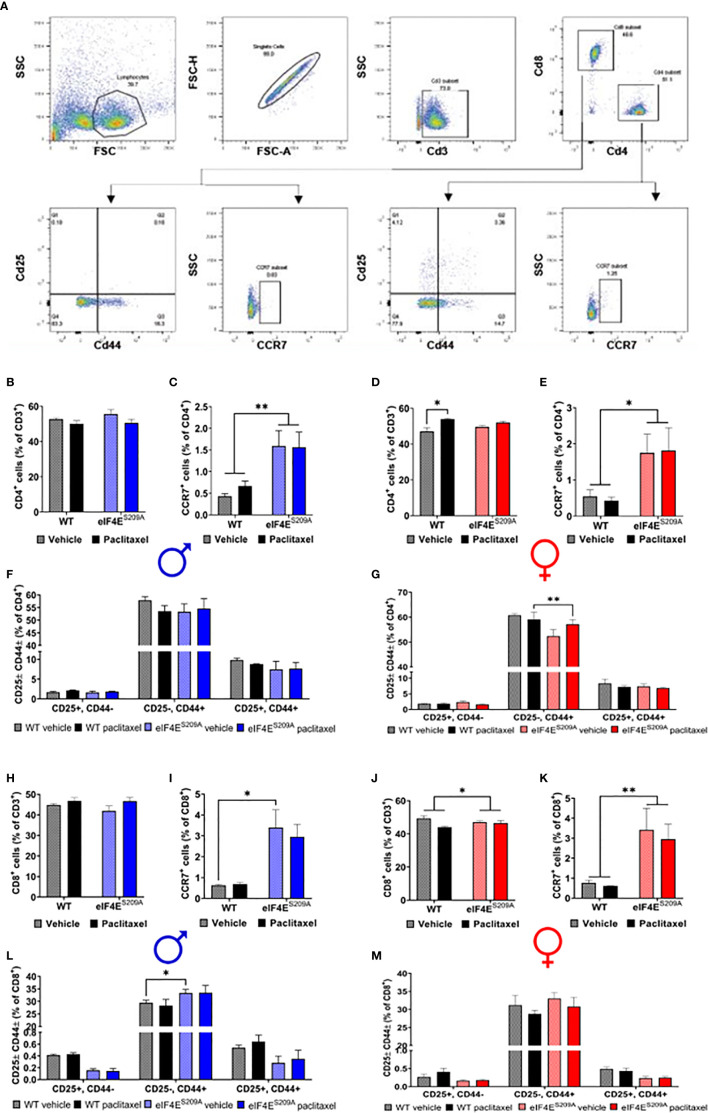
Figure 3.
Paclitaxel dysregulates CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subpopulations in an eIF4E-dependent manner. (A) Gating strategy used for flow cytometry of lymphocytes from popliteal and inguinal lymph nodes. T-cells were separated from the whole lymphoid cells population using CD3. CD3+ cells were then gated for CD4+ T-cell and CD8+ T-cells. For each of these subsets, cells were further gated for CCR7 or CD25 and CD44. (B) Quantification of CD4+ T-cells from the CD3 population from male mice. (C) CCR7+ T-cells from isolated CD4+ population in males, **p 0.0063. (D) CD4+ cells gated for CD25 and/or CD44 in males. (E) Quantification of CD4+ T-cells from the CD3+ population from female mice, *p 0.0101. (F) CCR7+ T-cells from isolated CD4+ population in female mice, *p 0.0250. (G) CD4+ cells gated for CD25 and/or CD44 in female mice, **p 0.0011. (H) Quantification of CD8+ T-cells from the CD3+ population from male mice. (I) CCR7+ T-cells from isolated CD8+ population in males, *p 0.0433. (J) CD8+ cells gated for CD25 and/or CD44 in males, *p 0.0396. (K) Quantification of CD8+ T-cells from the CD3 population from female mice, *p 0.041. (L) CCR7+ T-cells from isolated CD8+ population in female mice, **p 0.0097. (M) CD8+ cells gated for CD25 and/or CD44 in female mice. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean, n = 3 mice each for male/female WT vehicle-treated and WT paclitaxel groups, n = 4 mice each for male/female eIF4ES209A vehicle-treated and paclitaxel. Two-way ANOVA was performed with Tukey’s post-hoc for multiple comparisons.