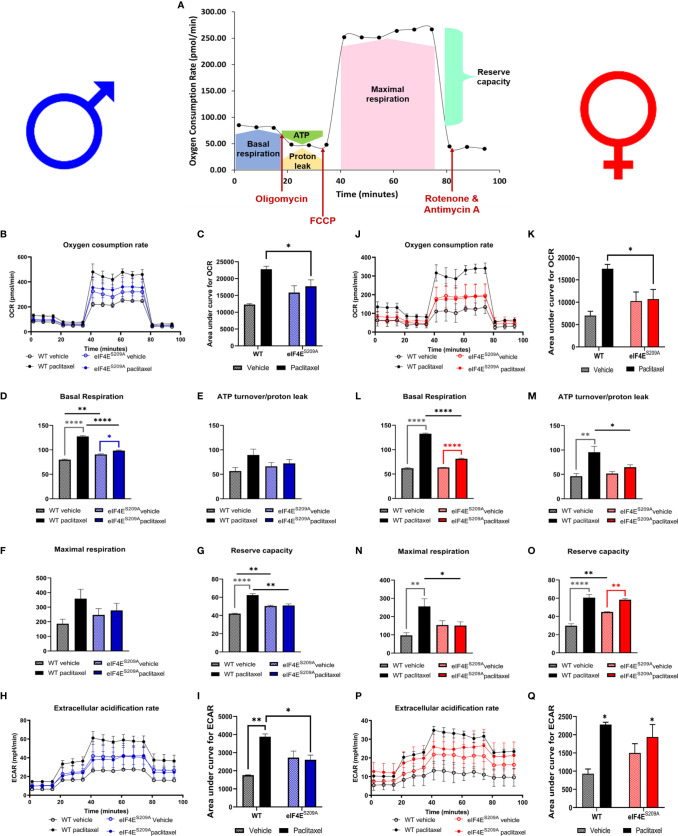
Figure 5.
Paclitaxel alters mitochondrial function of DRG neurons in an eIF4E-dependent manner. Dissociated dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons from WT and eIF4ES209A male and female mice were analyzed by the Seahorse Mito Stress test. (A) Graphic showing different phases of mitochondrial respiration. Adapted from the Agilent Seahorse XFp Cell Mito Test Kit User Guide published by Agilent Technologies. (B) Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) through phases of the Mito Stress test for male mice. (C) OCR data in male mice shown as area under the curve (AUC), *p 0.0136. (D-G) OCR data for male mice broken down into phases of mitochondrial respiration. Basal respiration: *p 0.0134, **p 0.0018, ****p<0.0001. Reserve capacity: **p 0.0063 for WT vs eIF4ES209A vehicle, **p 0.001 for WT vs eIF4ES209A paclitaxel. (H) Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) for male mice. (I) ECAR data in male mice shown as AUC, *p 0.0303 for WT vs eIF4ES209A vehicle, **p 0.0021 for WT vehicle vs WT paclitaxel groups. (J) OCR through phases of the Mito Stress test for female mice. (K) OCR data in female mice shown as AUC, *p 0.0455. (L–O) OCR data for female mice broken down into phases of mitochondrial respiration. Basal respiration: ****p<0.0001, ATP turnover: *p 0.0481, **p 0.0021, maximal respiration: *p 0.0417, **p 0.0011, reserve capacity: **p 0.0037 for WT vs eIF4ES209A vehicle, **p 0.074 for eIF4ES209A vehicle vs eIF4ES209A paclitaxel, ****p<0.0001. (P) ECAR for female mice. (Q) ECAR data in female mice shown as AUC, *p 0.0116 for both genotypes vehicle vs paclitaxel-treated groups. All data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean, n = 3-4 mice each for male/female WT vehicle-treated and WT paclitaxel groups, n = 4-7 mice each for male/female eIF4ES209A vehicle-treated and paclitaxel. For analyzing AUC data, two-way ANOVA was performed with Tukey’s post-hoc for multiple comparisons. For analyzing each phase of mitochondrial respiration, an ordinary one-way ANOVA was used with Sidak’s post-hoc for multiple comparisons.