Figure 8.
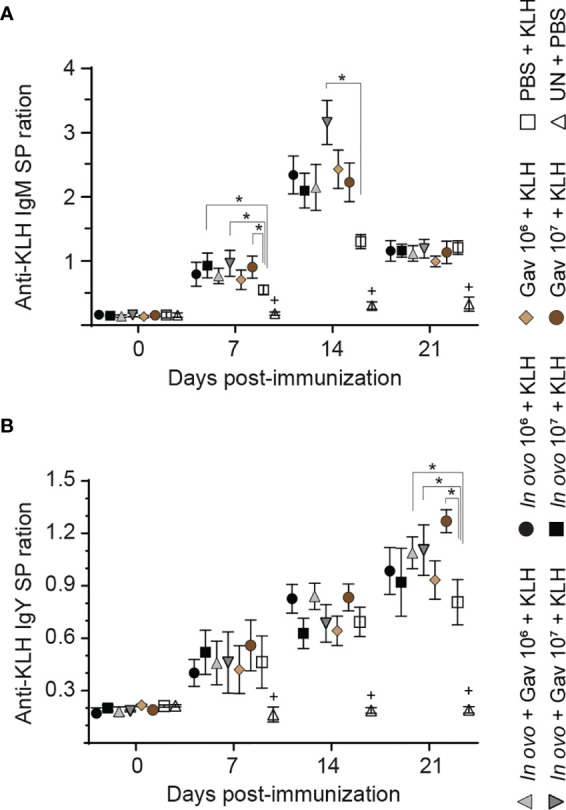
Serum anti-KLH antibodies titers as a measure of immune competence. Serum anti-KLH IgM (A) and IgY (B) titers were determined by indirect ELISA. Serum samples were collected post-hatch from chickens immunized with KLH and pre-treated with a lactobacilli cocktail as follow: groups 1 and 2 received 106 and 107 CFUs of lactobacilli cocktail in ovo, respectively, at embryonic day eighteen; groups 3 and 4 received 106 and 107 CFUs of lactobacilli, respectively, via both in ovo and oral gavage (on days 1, 7, 14, 21, 28 post-hatch); groups 5 and 6 received 106 and 107 CFUs of lactobacilli, respectively, via oral gavage; group 7 was injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS); group 8 remained untreated (UN). On days 14 and 21 post-hatch, birds were immunized intramuscularly with 100 μg KLH in 0.25 ml PBS. The untreated group (UN) was inoculated intramuscularly with 0.5 ml of PBS and served as the negative control. Statistical significance among treatment groups was calculated using SAS Proc GLM (General Linear Model) followed by Tukey’s comparison test. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean. Results were considered statistically significant if P < 0.05. Bars with asterisks represent a significant difference among treatments. The data are representative samples from 12 individual birds.
