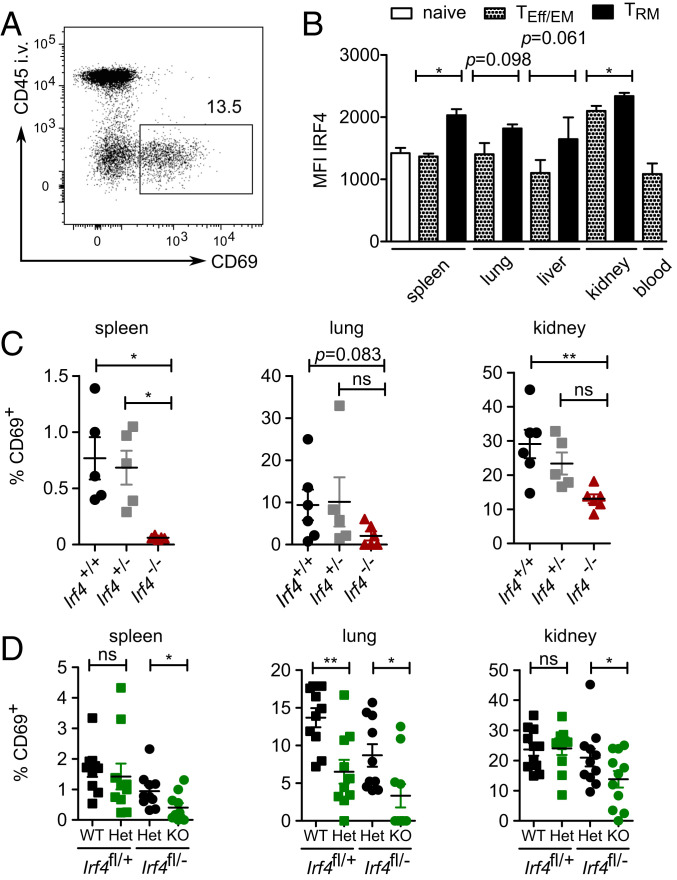
Fig. 6.
IRF4 supports survival of CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells. (A) Representative gating strategy for CD45IV− CD69+ CD8+ TRM cells in lung. (B) Irf4+/+ mice were infected with LmOVA. After 5 wk, tissues were analyzed for CD8+ T cells with a TRM phenotype. Mean fluorescence intensity of IRF4 staining of CD45IV− CD44+ CD62L− CD69− CD8+ T effector/effector memory (TEff/EM) cells, of CD45IV− CD44+ CD62L− CD69+ CD8+ TRM cells and corresponding CD45IV+ CD8+ TEff/EM cells in blood, and of CD44− CD62L+ naïve CD8+ T cells. Representative result of two independent experiments, each with three individually analyzed mice. Mean ± SEM, paired t test. (C) Irf4+/+, Irf4+/−, and Irf4−/− mice were infected with LmOVA. After 5 wk, tissues were analyzed. Frequencies of CD8+ T cells with a TRM-cell phenotype among CD45IV− CD8+ T cells. Pooled results from two independent experiments with five or six mice/group. Mean ± SEM, ANOVA, and Bonferroni’s post-test. (D) Rag1−/− mice were reconstituted with T cells from naïve Irf4fl/+×CreERT2 and Irf4fl/−×CreERT2 mice. Recipient mice were infected with LmOVA. After 5 wk, mice were treated with tamoxifen for 5 d. After 6 mo, tissues were analyzed for CD8+ T cells with a TRM phenotype among CD45IV− CD8+ T cells. Pooled results from two independent experiments with five and six mice. Mean ± SEM, paired t test. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01.