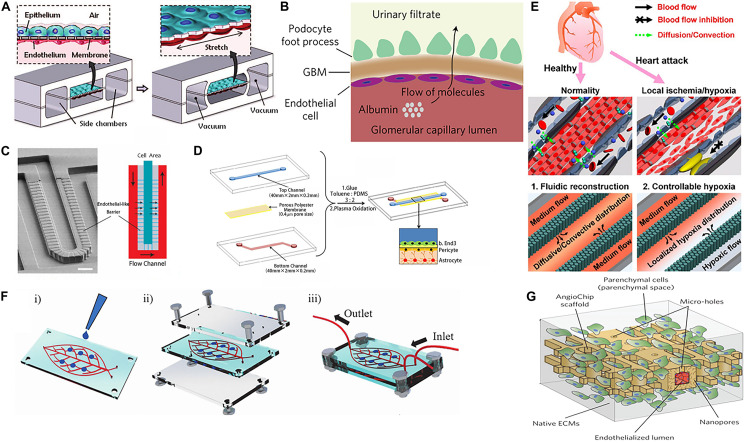
FIGURE 2.
Vascularization of organoids using various methods. (A) The alveolar epithelial cells and the vascular endothelial cells with flexible PDMS membrane form an alveolar-capillary barrier. Adapted from Huh et al. (2010). Reprinted with permission from AAAS. (B) Schematic representation of glomerular capillary wall with podocytes and endothelial cells that form a filtration barrier. (C) SEM micrograph and structure diagram of microfluidic chip simulates the hepatic sinusoid model. (D) Endothelial cells, pericytes, and astrocytes construct the blood–brain barrier (BBB). (E) The microfluidic device for studying controllable myocardial hypoxia and for myocardial fluidic microenvironment mimicking. (F) Human-on-leaf-chip simulates the complex vascular network structure of the human body. (G) AngioChip with branching interconnected lumen composed of POMaC and biological components.