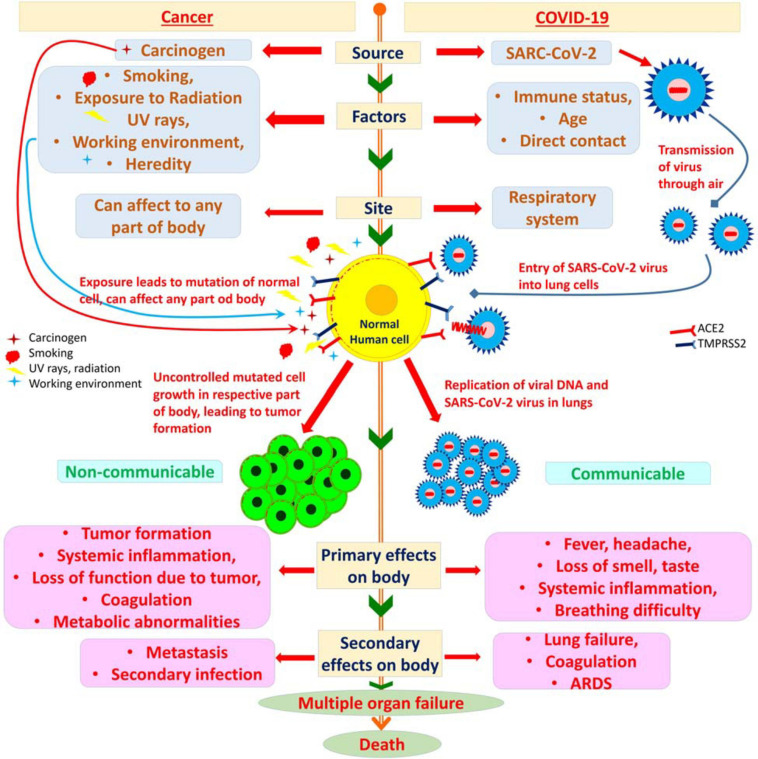
FIGURE 1.
Link between cancer and COVID-19. On the left, cancer progression is illustrated. Cancer is a disease caused by exposure to carcinogens, factors such as smoking, exposure to radiation, UV rays, working environment, and heredity can increase the risk of cancer. Any part of the body can be mutated resulting in cancer. After mutation there is uncontrolled growth of the mutated cells leading to the formation of a tumor, the tumor is non-communicable. Systemic inflammation, loss of function of the respective organ or part of body, coagulation, and metabolic abnormalities are the primary effects of cancer. As cancer progresses to advanced stages, metastasis along with increased susceptibility to secondary infections is observed leading to multiple organ failure and ultimately death. On the right, COVID-19 progression is illustrated. The source of COVID-19, a viral infection, is SARS-CoV-2, risk factors include immune status, age, and direct contact with the virus or infected person. The virus enters through the respiratory system into the human body and gets entry into the lung cells, where the replication of the virus occurs. COVID-19 is highly communicable and leads to fever, headache, loss of smell and taste, along with systemic inflammation and difficulty in breathing. Secondary infection to other organs is observed if the infection is chronic leading to lung failure, coagulation, and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Multiple organ failure leading ultimately to death is observed in COVID-19.